30. Time and Motion¶
Learn how to handle time and motion in Siv3D.
30.1 Measuring Elapsed Time¶
Scene::DeltaTime()returns the elapsed time from the previous frame (in seconds) as adoubletype- This value can be used to create motion that is independent of frame rate
- For details, see Tutorial 14
- Generally, if the elapsed time from the previous frame is too large, animation and physics simulation steps in the game become large, potentially compromising stability
- Therefore,
Scene::DeltaTime()is limited to not exceed the value ofScene::GetMaxDeltaTime()(default is0.1)
30.2 Accumulating Elapsed Time¶
Scene::Time()returns the elapsed time since the program started (in seconds) as adoubletype- It is updated when
System::Update()is called, so calls toScene::Time()within the same frame return the same value

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
while (System::Update())
{
font(U"Time: {:.2f}"_fmt(Scene::Time())).draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 40 }, ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
- The value returned by
Scene::Time()is the accumulation ofScene::DeltaTime() - As mentioned above,
Scene::DeltaTime()may be shorter than the actual frame elapsed time, soScene::Time()may be shorter than real time passage - When time synchronized with reality is needed, use the following methods:
- Use
Stopwatchto measure time - Use
Timerto measure time - Use
Time::GetMillisec()to get real time points
- Use
30.3 Time-Based Motion¶
- You can express motion by changing position, size, angle, etc. over time
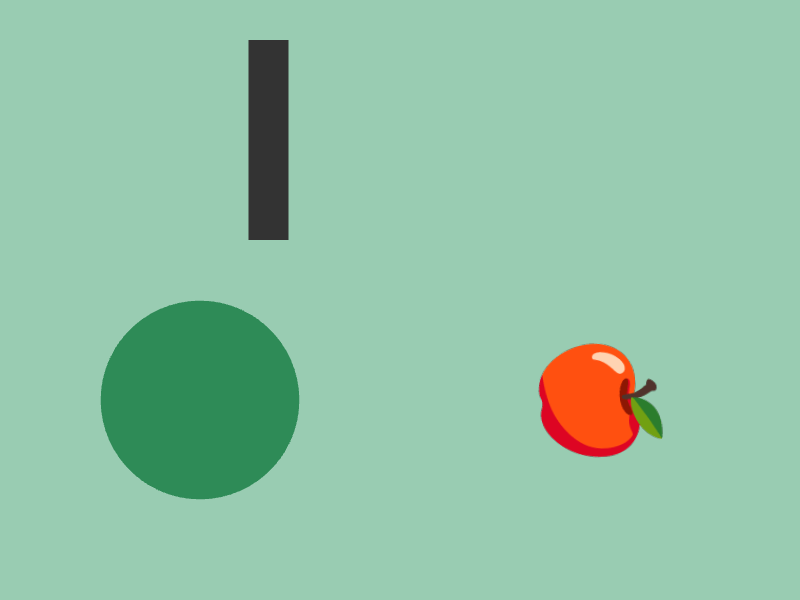
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
const Texture emoji{ U"🍎"_emoji };
while (System::Update())
{
const double t = Scene::Time();
RectF{ (t * 50), 40, 40, 200 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ 200, 400, (t * 20) }.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
emoji.rotated(t * 90_deg).drawAt(600, 400);
}
}
30.4 Doing Something at Regular Intervals¶
- Decide on an event period in advance, and trigger the event when accumulated time (seconds) exceeds that period (seconds)

Count up every 0.5 seconds
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const double interval = 0.5;
double accumulatedTime = 0.0;
int32 count = 0;
while (System::Update())
{
accumulatedTime += Scene::DeltaTime();
if (interval <= accumulatedTime)
{
Print << ++count;
accumulatedTime -= interval;
}
}
}
- When the event period is short (shorter than one frame's time), multiple events need to be triggered within one frame
- To handle such situations, use
while (eventPeriod <= accumulatedTime)instead ofif

Count up every 0.01 seconds
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const double interval = 0.01;
double accumulatedTime = 0.0;
int32 count = 0;
while (System::Update())
{
accumulatedTime += Scene::DeltaTime();
while (interval <= accumulatedTime)
{
Print << ++count;
accumulatedTime -= interval;
}
}
}
30.5 Stopwatch¶
Stopwatchis a class that conveniently measures elapsed time and resets- Specifying
StartImmediately::Yesin theStopwatchconstructor starts measurement immediately upon creation - The main member functions of
Stopwatchare as follows:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
.start() |
Start or resume measurement |
.pause() |
Pause measurement |
.resume() |
Resume paused measurement |
.reset() |
Stop measurement and reset elapsed time to 0 |
.restart() |
Reset measurement and start measuring from 0 again |
.isRunning() |
Returns bool indicating whether measurement is in progress |
.isPaused() |
Returns bool indicating whether measurement is paused |
.isStarted() |
Returns bool indicating whether measurement has started |
.min() |
Returns elapsed time in minutes as int32 |
.s() |
Returns elapsed time in seconds as int32 |
.s64() |
Returns elapsed time in seconds as int64 |
.sF() |
Returns elapsed time in seconds as double |
.ms() |
Returns elapsed time in milliseconds as int32 |
.ms64() |
Returns elapsed time in milliseconds as int64 |
.msF() |
Returns elapsed time in milliseconds as double |
.us() |
Returns elapsed time in microseconds as int32 |
.us64() |
Returns elapsed time in microseconds as int64 |
.usF() |
Returns elapsed time in microseconds as double |
.format(...) |
Returns elapsed time as a string in the specified format |
- Elapsed time is not affected by
Scene::GetMaxDeltaTime()and is always measured in real time - There's no need to get elapsed time by individual units
- When elapsed time is 65.4 seconds,
s()returns65,sF()returns65.4, andms()returns65400
- When elapsed time is 65.4 seconds,
- When called multiple times within the same frame, elapsed time may vary depending on timing

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
// Start measurement immediately upon creation
Stopwatch stopwatch{ StartImmediately::Yes };
while (System::Update())
{
if (MouseL.down())
{
if (stopwatch.isPaused())
{
// Resume
stopwatch.resume();
}
else
{
// Pause
stopwatch.pause();
}
}
if (MouseR.down())
{
// Restart
stopwatch.restart();
}
RectF{ 0, 200, (stopwatch.sF() * 100), 200 }.draw();
font(stopwatch.format(U"mm:ss.xx")).draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 40 }, ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
30.6 Time Types¶
- The following types are available to represent time:
- Types with
Fhold values as floating point numbers Durationis an alias forSecondsF
- Types with
| Type | Time Represented |
|---|---|
Days or DaysF |
Days |
Hours or HoursF |
Hours |
Minutes or MinutesF |
Minutes |
Seconds or SecondsF |
Seconds |
Milliseconds or MillisecondsF |
Milliseconds |
Microseconds or MicrosecondsF |
Microseconds |
Nanoseconds or NanosecondsF |
Nanoseconds |
Duration |
Alias for SecondsF |
- You can easily create time types by adding time literal suffixes to integer or floating point literals
- For example,
10sis the same asSeconds{ 10 }, and0.5sis the same asSecondsF{ 0.5 }
- For example,
| Suffix | Time |
|---|---|
_d |
Days |
h |
Hours |
min |
Minutes |
s |
Seconds |
ms |
Milliseconds |
us |
Microseconds |
ns |
Nanoseconds |
- Time types support arithmetic and comparison operations
- Time types can be converted between each other
- Converting from floating point time types → integer time types requires
DurationCast<Type>()
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const MinutesF m = 3min;
const SecondsF s = 5.5s;
Print << (m + s);
const Seconds s2 = DurationCast<Seconds>(s);
Print << s2;
const Duration d = 123.456s;
Print << d;
while (System::Update())
{
}
}
30.7 Timer¶
Timeris a class that measures remaining time with countdown from a specified time- Specifying
StartImmediately::Yesin theTimerconstructor starts measurement immediately upon creation - The main member functions of
Timerare as follows:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
.start() |
Start or resume the timer |
.pause() |
Pause the timer |
.resume() |
Resume the paused timer |
.reset() |
Stop the timer and reset remaining time |
.restart() |
Reset the timer and start again |
.isRunning() |
Returns bool indicating whether measurement is in progress |
.isPaused() |
Returns bool indicating whether measurement is paused |
.isStarted() |
Returns bool indicating whether measurement has started |
.reachedZero() |
Returns bool indicating whether remaining time has reached 0 |
.min() |
Returns remaining time in minutes as int32 |
.s() |
Returns remaining time in seconds as int32 |
.s64() |
Returns remaining time in seconds as int64 |
.sF() |
Returns remaining time in seconds as double |
.ms() |
Returns remaining time in milliseconds as int32 |
.ms64() |
Returns remaining time in milliseconds as int64 |
.msF() |
Returns remaining time in milliseconds as double |
.us() |
Returns remaining time in microseconds as int32 |
.us64() |
Returns remaining time in microseconds as int64 |
.usF() |
Returns remaining time in microseconds as double |
.progress1_0() |
Returns timer progress (starts at 1.0, ends at 0.0) as double |
.progress0_1() |
Returns timer progress (starts at 0.0, ends at 1.0) as double |
- Remaining time is not affected by
Scene::GetMaxDeltaTime()and is always measured in real time - There's no need to get remaining time by individual units
- When remaining time is 65.4 seconds,
s()returns65,sF()returns65.4, andms()returns65400
- When remaining time is 65.4 seconds,

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
// Start measurement immediately upon creation
Timer timer{ 10s, StartImmediately::Yes };
while (System::Update())
{
if (MouseL.down())
{
if (timer.isPaused())
{
// Resume
timer.resume();
}
else
{
// Pause
timer.pause();
}
}
if (MouseR.down())
{
// Restart
timer.restart();
}
RectF{ 0, 200, (timer.progress1_0() * 800), 200 }.draw();
if (timer.reachedZero())
{
font(U"Time's up!").draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 40 }, Palette::Red);
}
else
{
font(timer.format(U"mm:ss.xx")).draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 40 }, ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
}
30.8 Time Comparison¶
- You can compare
StopwatchorTimerobjects with time type values - Instead of
if (3 <= stopwatch.s()), you can useif (3s <= stopwatch)to check if the stopwatch has elapsed 3 seconds or more - Instead of
if (timer.sF() < 10.0), you can useif (timer < 10s)to check if the timer has less than 10 seconds remaining
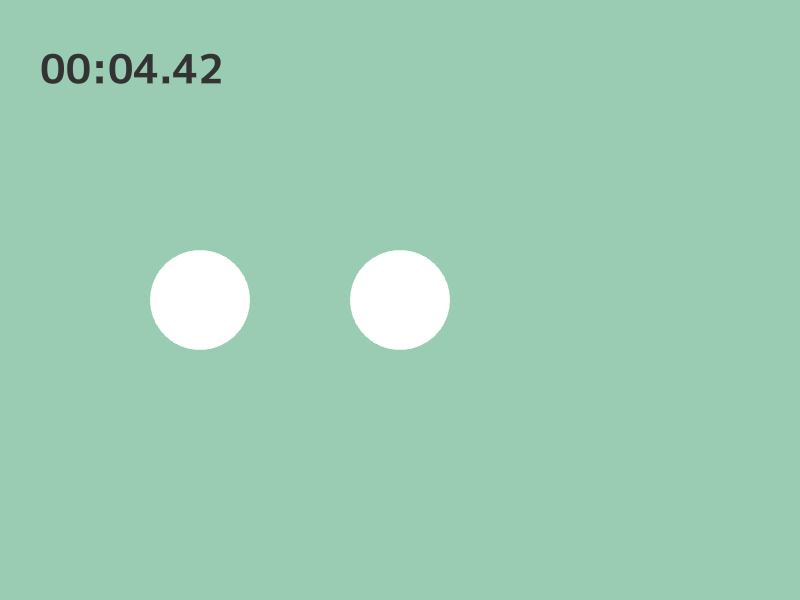
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
// Start measurement immediately upon creation
Stopwatch stopwatch{ StartImmediately::Yes };
while (System::Update())
{
// If 2 seconds or more have elapsed
if (2s <= stopwatch)
{
Circle{ 200, 300, 50 }.draw();
}
// If 4 seconds or more have elapsed
if (4s <= stopwatch)
{
Circle{ 400, 300, 50 }.draw();
}
// If 6 seconds or more have elapsed
if (6s <= stopwatch)
{
Circle{ 600, 300, 50 }.draw();
}
font(stopwatch.format(U"mm:ss.xx")).draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 40 }, ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
30.9 Periodic Motion¶
- When you need values that periodically change between 0 ↔ 1 or -1 ↔ 1, it's convenient to use periodic functions provided in the
Periodic::namespace - These functions return values in the range 0~1 or -1~1 with specific periods and patterns based on time passage
Periodic::function(period, elapsed time)- The period is specified using time literals like
2sor0.5s - Elapsed time (seconds) is passed as
doubletype. By default,Scene::Time()is used
- The period is specified using time literals like
| Periodic Function | Motion |
|---|---|
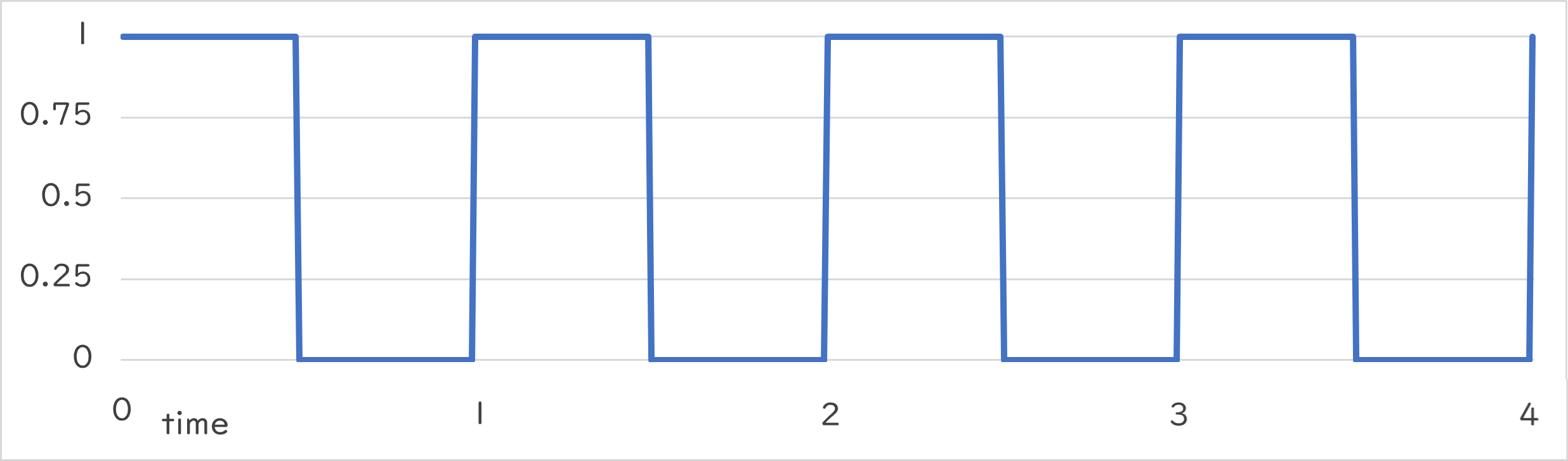
Periodic::Square0_1 |
 |
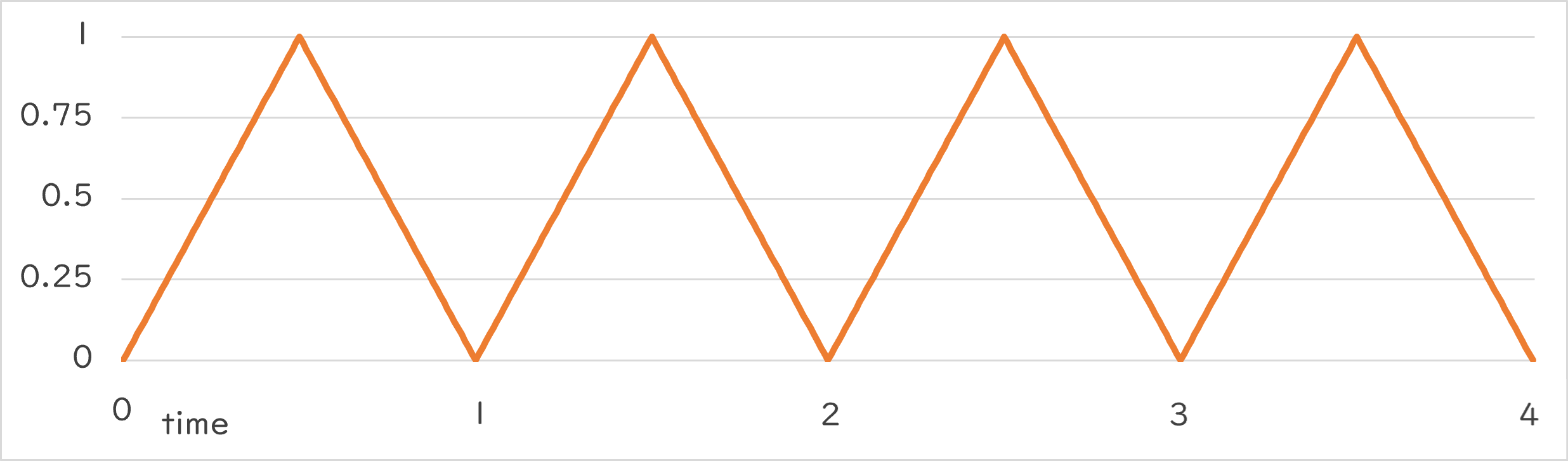
Periodic::Triangle0_1 |
 |
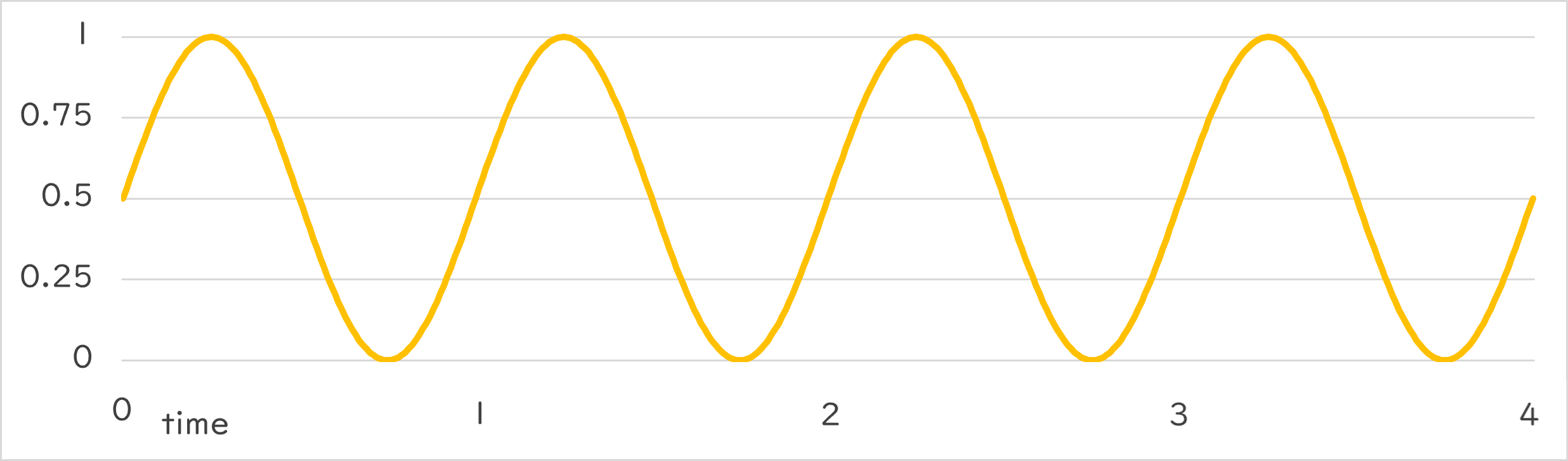
Periodic::Sine0_1 |
 |
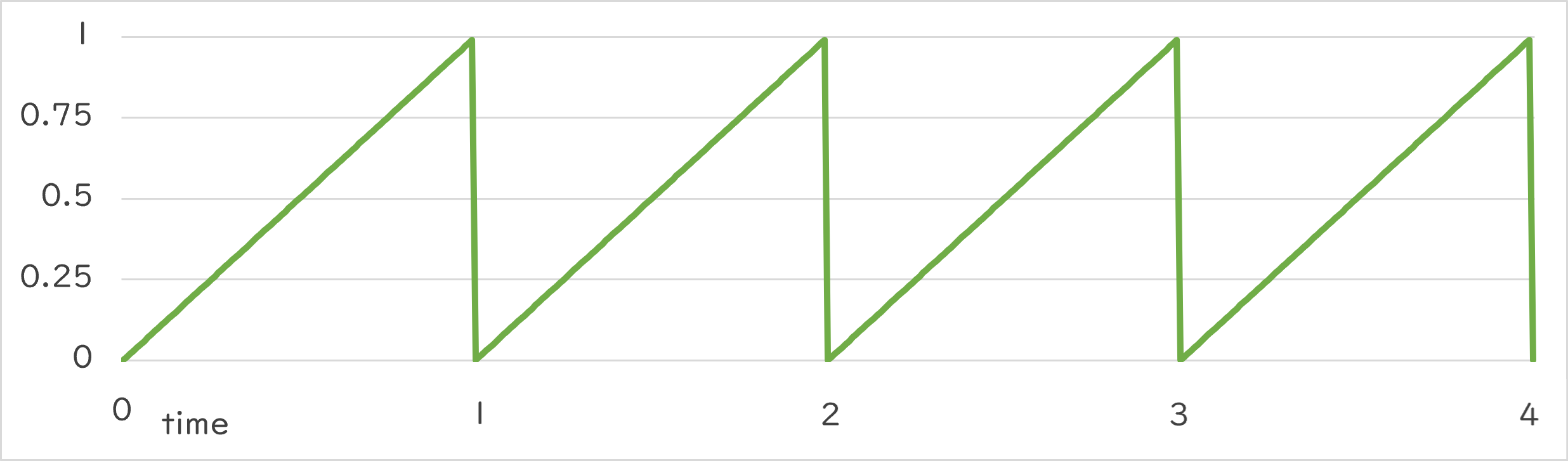
Periodic::Sawtooth0_1 |
 |
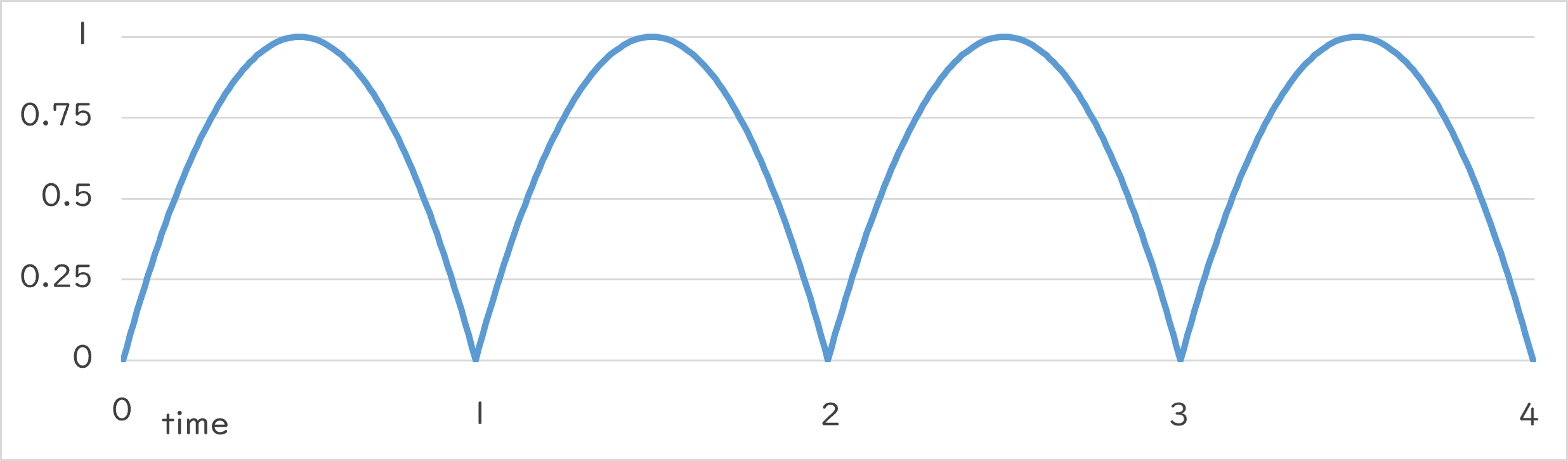
Periodic::Jump0_1 |
 |
Periodic::Square0_1()¶
- Returns 0.0 or 1.0 alternately at the specified period
- Returns 1.0 in the first half of the period and 0.0 in the remaining half
Periodic::Triangle0_1()¶
- Repeats the change from 0.0 increasing at constant speed to 1.0, then decreasing at constant speed back to 0.0 at the specified period
Periodic::Sine0_1()¶
- Returns numeric changes that draw a sine curve in the range 0.0~1.0 at the specified period
Periodic::Sawtooth0_1()¶
- Repeats the change from 0.0 → 1.0 at the specified period
Periodic::Jump0_1()¶
- Repeats numeric changes like velocity when jumping from the ground at the specified period
Sample Code¶
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
while (System::Update())
{
const double p0 = Periodic::Square0_1(2s);
const double p1 = Periodic::Triangle0_1(2s);
const double p2 = Periodic::Sine0_1(2s);
const double p3 = Periodic::Sawtooth0_1(2s);
const double p4 = Periodic::Jump0_1(2s);
Line{ 100, 0, 100, 600 }.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.2 });
Line{ 700, 0, 700, 600 }.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (100 + p0 * 600), 100, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (100 + p1 * 600), 200, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (100 + p2 * 600), 300, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (100 + p3 * 600), 400, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (100 + p4 * 600), 500, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
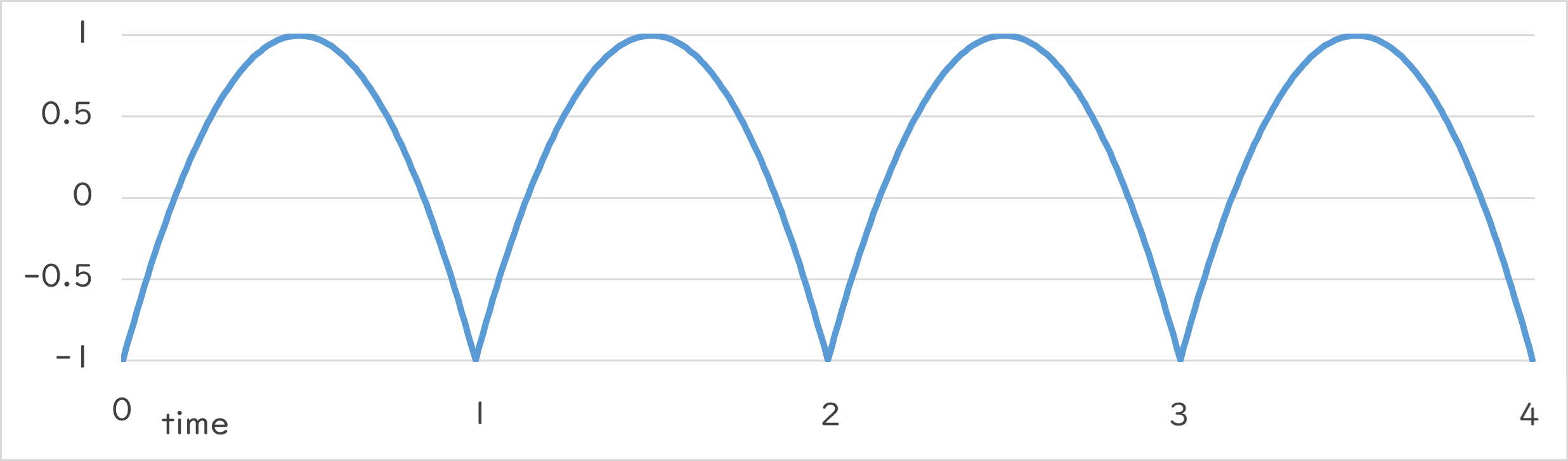
| Periodic Function | Motion |
|---|---|
Periodic::Square1_1 |
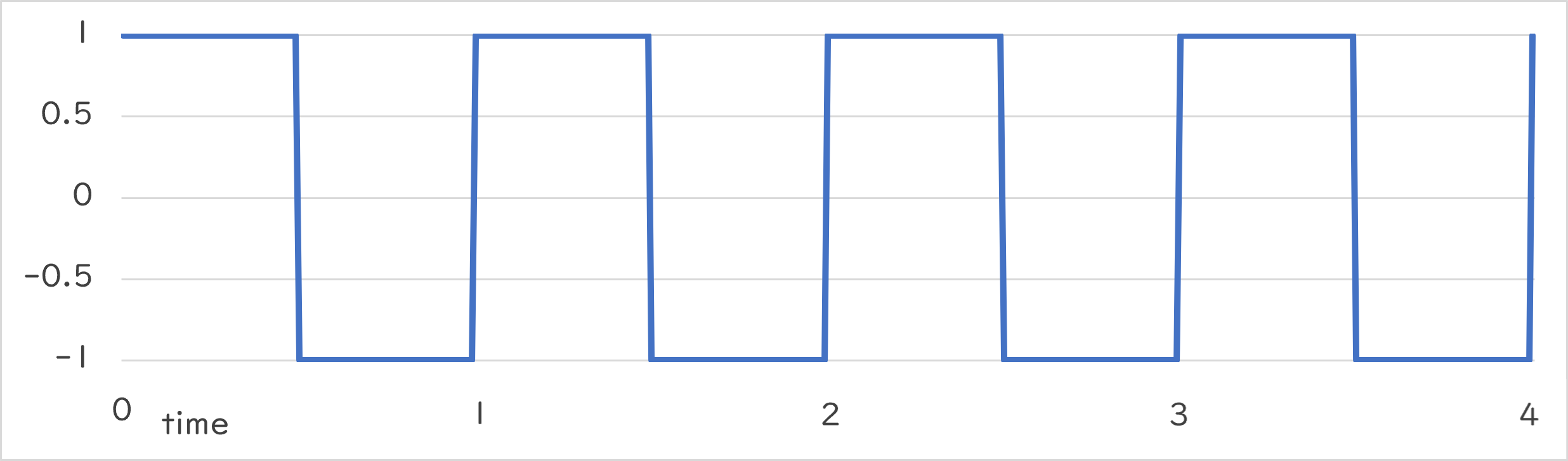 |
Periodic::Triangle1_1 |
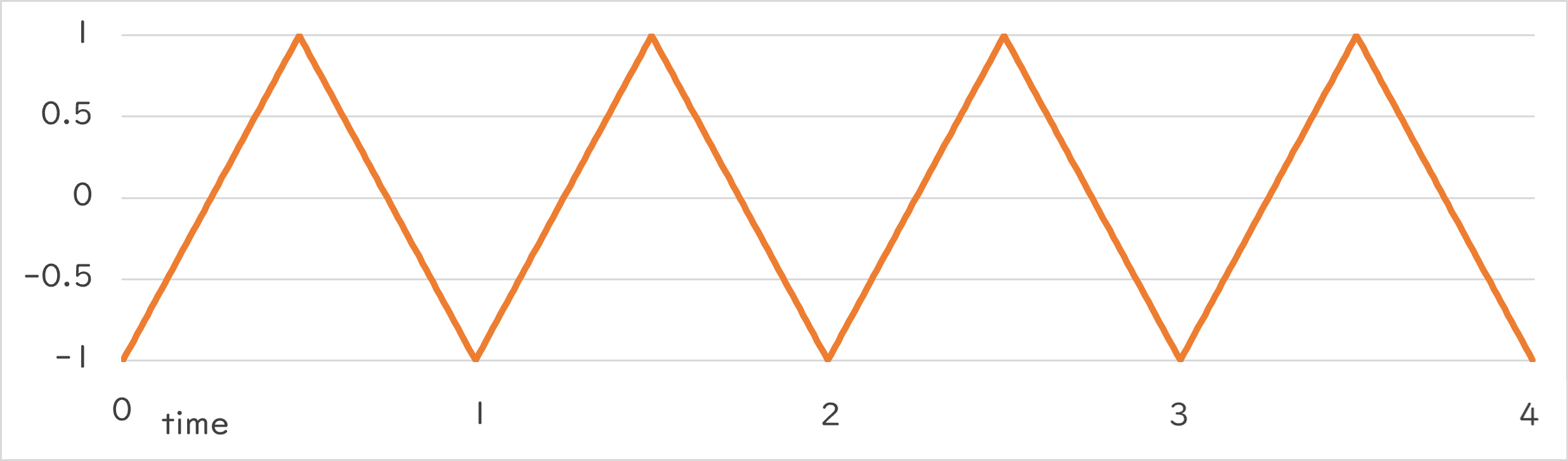 |
Periodic::Sine1_1 |
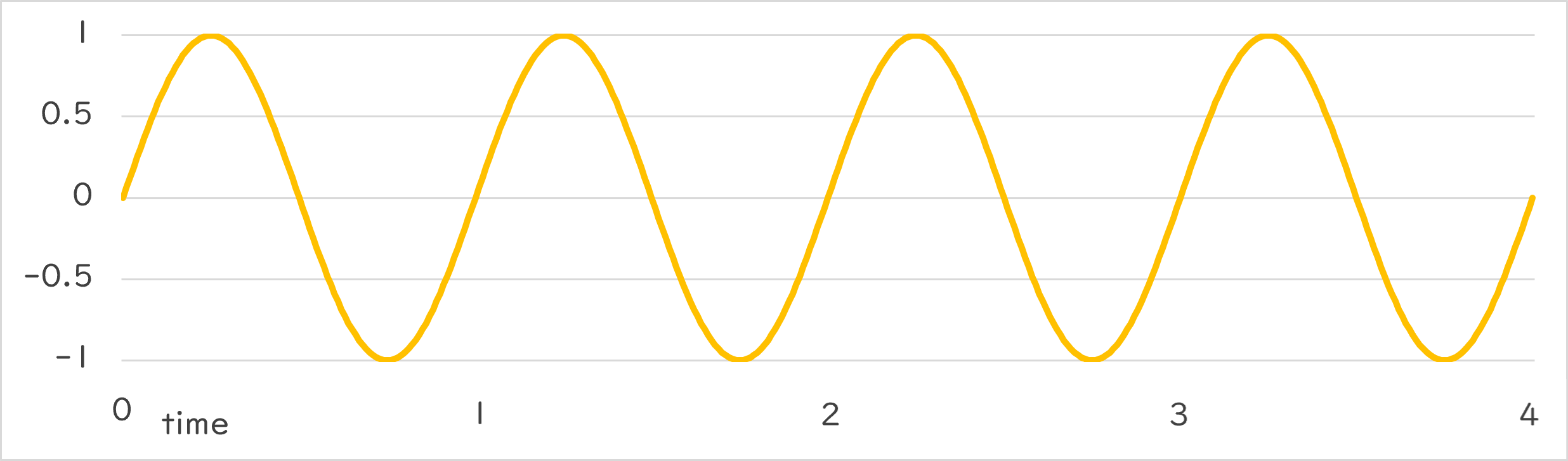 |
Periodic::Sawtooth1_1 |
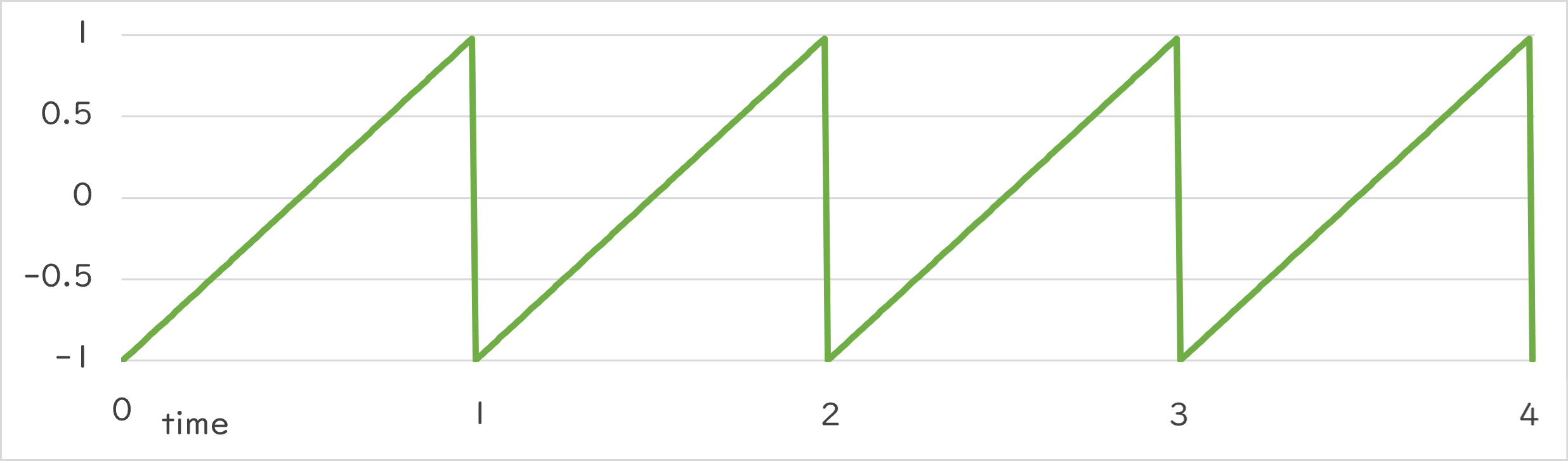 |
Periodic::Jump1_1 |
 |
Periodic::Square1_1()¶
- Returns -1.0 or 1.0 alternately at the specified period
- Returns 1.0 in the first half of the period and -1.0 in the remaining half
Periodic::Triangle1_1()¶
- Repeats the change from -1.0 increasing at constant speed to 1.0, then decreasing at constant speed back to -1.0 at the specified period
Periodic::Sine1_1()¶
- Returns numeric changes that draw a sine curve in the range -1.0~1.0 at the specified period
Periodic::Sawtooth1_1()¶
- Repeats the change from -1.0 → 1.0 at the specified period
Periodic::Jump1_1()¶
- Repeats numeric changes like velocity when jumping from the ground at the specified period
Sample Code¶

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
while (System::Update())
{
const double p0 = Periodic::Square1_1(2s);
const double p1 = Periodic::Triangle1_1(2s);
const double p2 = Periodic::Sine1_1(2s);
const double p3 = Periodic::Sawtooth1_1(2s);
const double p4 = Periodic::Jump1_1(2s);
Line{ 100, 0, 100, 600 }.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.2 });
Line{ 700, 0, 700, 600 }.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (400 + p0 * 300), 100, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (400 + p1 * 300), 200, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (400 + p2 * 300), 300, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (400 + p3 * 300), 400, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
Circle{ (400 + p4 * 300), 500, 20 }.draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
30.10 Transition¶
- When you need to process "gradually approach 1.0 while a condition is met, gradually return to 0.0 when the condition is not met," the
Transitionclass is convenient - The
Transitionconstructor sets the minimum time required to reach from 0.0 to 1.0 and the minimum time to decrease from maximum to minimum value - Call
.update(state)every frame, passingtruefor increase andfalsefor decrease, and the value will increase/decrease at the set speed - You can get the current value with
.value()

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
Transition transition{ 1.0s, 0.25s };
while (System::Update())
{
// Increase if left mouse button is pressed, otherwise decrease
transition.update(MouseL.pressed());
RectF{ 0, 200, (transition.value() * 800), 200 }.draw();
font(U"{:.2f}"_fmt(transition.value())).draw(40, Vec2{ 40, 40 }, ColorF{0.2});
}
}
30.11 Linear Interpolation¶
- When you have states A and B and want to interpolate between them with interpolation coefficient
t, useA.lerp(B, t) - The interpolation coefficient
tis usually in the range 0.0 ~ 1.0 - The following classes have the member function
.lerp():
| Element | Class |
|---|---|
| Color | ColorF, HSV |
| Vector | Point, Vec2, Vec3, Vec4 |
| Shape | Line, Circle, Rect, RectF, Triangle, Quad, Ellipse, RoundRect |
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const ColorF color0{ 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 };
const ColorF color1{ 0.1, 1.0, 0.5 };
const Circle circle0{ 100, 200, 20 };
const Circle circle1{ 700, 200, 40 };
const RectF rect0{ Arg::center(100, 300), 80 };
const RectF rect1{ Arg::center(700, 300), 40 };
const Triangle triangle0{ 100, 400, 100, 0_deg };
const Triangle triangle1{ 700, 400, 100, 120_deg };
const Line line0{ 50, 450, 150, 550 };
const Line line1{ 750, 450, 650, 550 };
while (System::Update())
{
const double t = Periodic::Triangle0_1(3s);
RectF{ 200, 50, 400, 80 }.draw(color0.lerp(color1, t));
circle0.lerp(circle1, t).draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
rect0.lerp(rect1, t).draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
triangle0.lerp(triangle1, t).draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
line0.lerp(line1, t).draw(2, ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
30.12 Easing¶
- Simply increasing values linearly (at constant speed) from 0.0 to 1.0 results in monotonous motion
- Adding speed variations, such as gradually accelerating at the beginning and slowing down near the goal, can achieve sophisticated visual effects
- Easing functions that can transform 0.0 ↔ 1.0 movement into characteristic curves can improve motion impressions
- About 30 types of easing functions are available, and you can check the list at Easing Functions Cheat Sheet
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// Start position
Vec2 from{ 100, 100 };
// Goal position
Vec2 to{ 700, 500 };
Stopwatch stopwatch{ StartImmediately::Yes };
while (System::Update())
{
// Movement ratio 0.0~1.0
const double t = Min(stopwatch.sF(), 1.0);
// Apply easing function
const double e = EaseInOutExpo(t);
// Position progressed by ratio e from start to goal position
const Vec2 pos = from.lerp(to, e);
if (MouseL.down())
{
// Set start position to current position
from = pos;
// Set goal position to mouse cursor position
to = Cursor::Pos();
stopwatch.restart();
}
pos.asCircle(40).draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
to.asCircle(50).drawFrame(5, ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
30.13 SmoothDamp¶
- Linear interpolation and easing are suitable for cases where start and end values (target values) are fixed
- However, when the target value changes during movement, speed and direction change abruptly, giving an unnatural impression
- To continue smooth movement/change considering current velocity even when target values change, use the
Math::SmoothDampfunction - The
Math::SmoothDampfunction is a very convenient and powerful interpolation function that calculates the next position based on time from current position, target position, and current velocity - The following types support the
Math::SmoothDampfunction:
| Element | Type/Class |
|---|---|
| Numeric types | float, double |
| Vector | Vec2, Vec3, Vec4 |
| Color | ColorF |
- More classes are planned to be supported in Siv3D v0.8
Function Overview¶
- The
Math::SmoothDampfunction forVec2is as follows:
Vec2 Math::SmoothDamp(const Vec2& from, const Vec2& to, Vec2& velocity, double smoothTime, const Optional<double>& maxSpeed = unspecified, double deltaTime = Scene::DeltaTime());`
from: Current positionto: Target positionvelocity: Current velocity (pass the variable storing velocity by reference)smoothTime: Smoothing time (expected time required when moving toward target at maximum speed). Delay time when chasing a moving target; smaller values reach the target fastermaxSpeed: Maximum speed. Specifyunspecifiedfor unlimiteddeltaTime: Elapsed time from previous frame (default isScene::DeltaTime())- Return value: Next position
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// Current position
Vec2 currentPos{ 100, 100 };
// Movement velocity
Vec2 velocity{ 0, 0 };
while (System::Update())
{
// Target position
const Vec2 targetPos = Cursor::Pos();
currentPos = Math::SmoothDamp(currentPos, targetPos, velocity, 0.5);
currentPos.asCircle(40).draw(ColorF{ 0.2 });
targetPos.asCircle(50).drawFrame(4, ColorF{ 0.2 });
}
}
30.14 Getting Application Launch Time¶
- To get the elapsed time since application startup in real time, use the following functions:
- Return value is
uint64type
- Return value is
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Time::GetSec() |
Returns elapsed time since application startup in seconds |
Time::GetMillisec() |
Returns elapsed time since application startup in milliseconds |
Time::GetMicrosec() |
Returns elapsed time since application startup in microseconds |
Time::GetNanosec() |
Returns elapsed time since application startup in nanoseconds |
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
while (System::Update())
{
ClearPrint();
Print << Time::GetSec();
Print << Time::GetMillisec();
Print << Time::GetMicrosec();
Print << Time::GetNanosec();
}
}
30.15 Getting UNIX Time¶
- To get the elapsed time since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 (UNIX epoch) (UNIX time), use the following functions:
- Return value is
uint64type
- Return value is
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
Time::GetSecSinceEpoch() |
Returns current UNIX time in seconds |
Time::GetMillisecSinceEpoch() |
Returns current UNIX time in milliseconds |
Time::GetMicrosecSinceEpoch() |
Returns current UNIX time in microseconds |
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
while (System::Update())
{
ClearPrint();
Print << Time::GetSecSinceEpoch();
Print << Time::GetMillisecSinceEpoch();
Print << Time::GetMicrosecSinceEpoch();
}
}
30.16 Date and Time Class¶
- A class
DateTimeis provided for handling dates and times
struct DateTime
{
int32 year;
int32 month;
int32 day;
int32 hour;
int32 minute;
int32 second;
int32 milliseconds;
};
- Addition and subtraction can be performed using time type values
DateTime::Now()returns the current date and time asDateTimetype
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
// Get current date and time
const DateTime t = DateTime::Now();
Print << t;
Print << t.year;
Print << t.month;
Print << t.day;
Print << t.hour;
Print << t.minute;
Print << t.second;
Print << t.milliseconds;
// 30 minutes ago
Print << (t - 30min);
// Next week
Print << (t + 7_d);
// Time until 2030
const Duration s = (DateTime{ 2030, 1, 1 } - t);
Print << s;
Print << DaysF{ s };
Print << DurationCast<Days>(s);
while (System::Update())
{
}
}
30.17 Getting Time Zone Offset¶
Time::UTCOffsetMinutes()returns the time zone offset in minutes from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) for the computer being used