45. Shape Intersection Detection¶
Learn how to perform click detection on shapes and intersection testing.
45.1 Mouse Over¶
- Using the member function
.mouseOver()of each shape class, you can check if the mouse cursor is over that shape .mouseOver()returns true when the mouse cursor is over the shape- Whether the shape is actually drawn does not affect the result
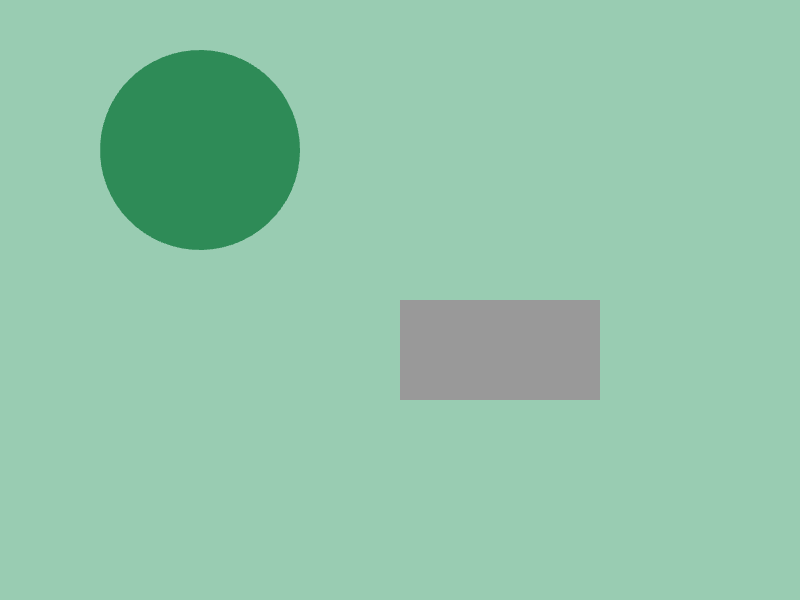
Change the color of a shape when the mouse cursor is over it
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Circle circle{ 200, 150, 100 };
const Rect rect{ 400, 300, 200, 100 };
while (System::Update())
{
circle.draw(circle.mouseOver() ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
rect.draw(rect.mouseOver() ? ColorF{ 0.8 } : ColorF{ 0.6 });
}
}
45.2 Shape Clicking¶
- Each shape class has the following member functions for click detection:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
.leftClicked() |
Whether the left mouse button was clicked on the shape |
.leftPressed() |
Whether the left mouse button is being pressed on the shape |
.leftReleased() |
Whether the left mouse button was released on the shape |
.rightClicked() |
Whether the right mouse button was clicked on the shape |
.rightPressed() |
Whether the right mouse button is being pressed on the shape |
.rightReleased() |
Whether the right mouse button was released on the shape |
- The relationship between click, pressed, and released is the same as
.down(),.pressed(), and.up()ofInput- For example,
.leftClicked()returnstrueonly in the frame when clicked .leftPressed()returnstruenot only in the frame when clicked, but also while continuing to be pressed thereafter.leftReleased()returnstrueonly in the frame when the click is released
- For example,
- When moving the cursor outside the shape area while holding down a mouse button,
.leftPressed()does not returntrue - When releasing the button outside the shape area,
.leftReleased()does not returntrue
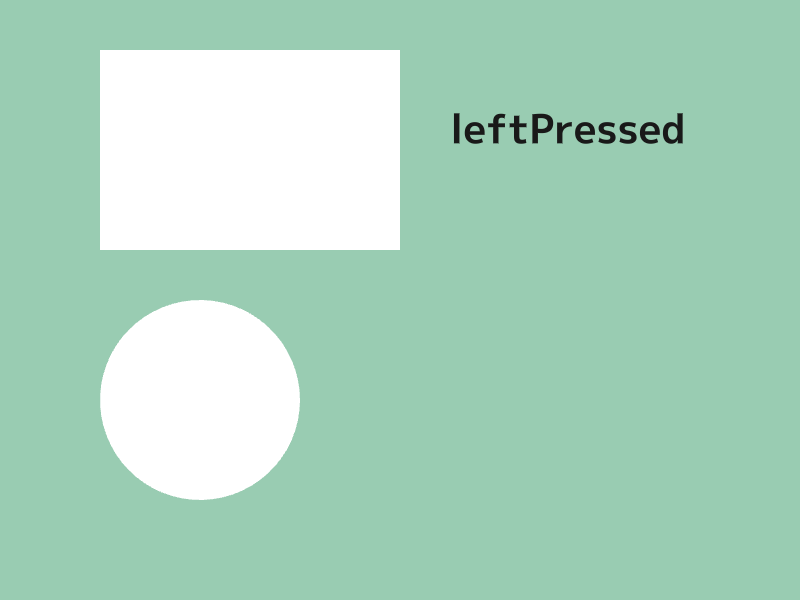
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 300, 200 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
while (System::Update())
{
rect.draw();
circle.draw();
if (rect.leftClicked())
{
font(U"leftClicked").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 50 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (rect.leftPressed())
{
font(U"leftPressed").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 100 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (rect.leftReleased())
{
font(U"leftReleased").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 150 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (circle.leftClicked())
{
font(U"leftClicked").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 350 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (circle.leftPressed())
{
font(U"leftPressed").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 400 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (circle.leftReleased())
{
font(U"leftReleased").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 450 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
}
45.3 Shape Intersection¶
- Whether two shapes
aandbintersect can be checked witha.intersects(b) - Detection is possible between different shape classes
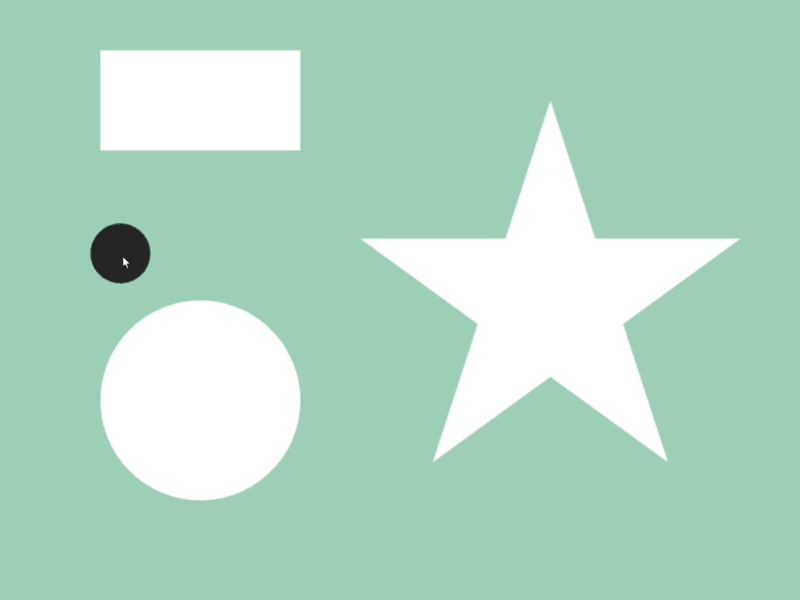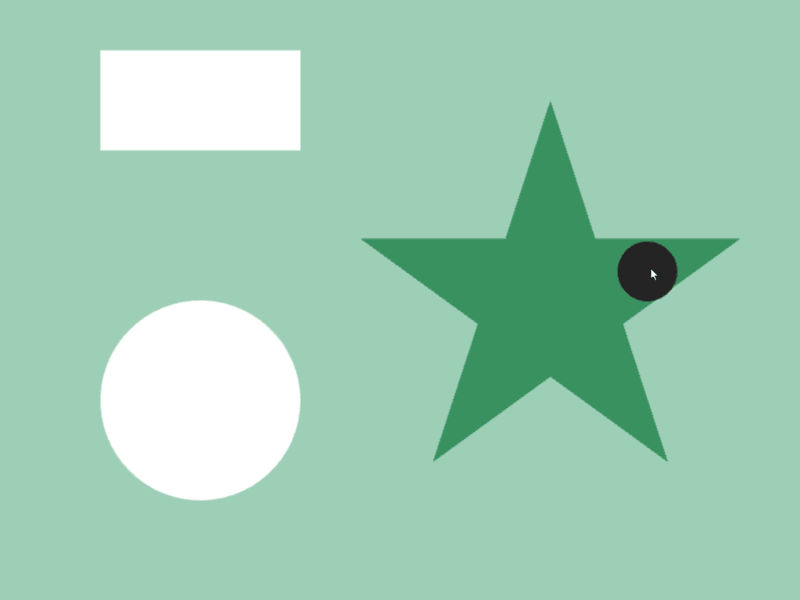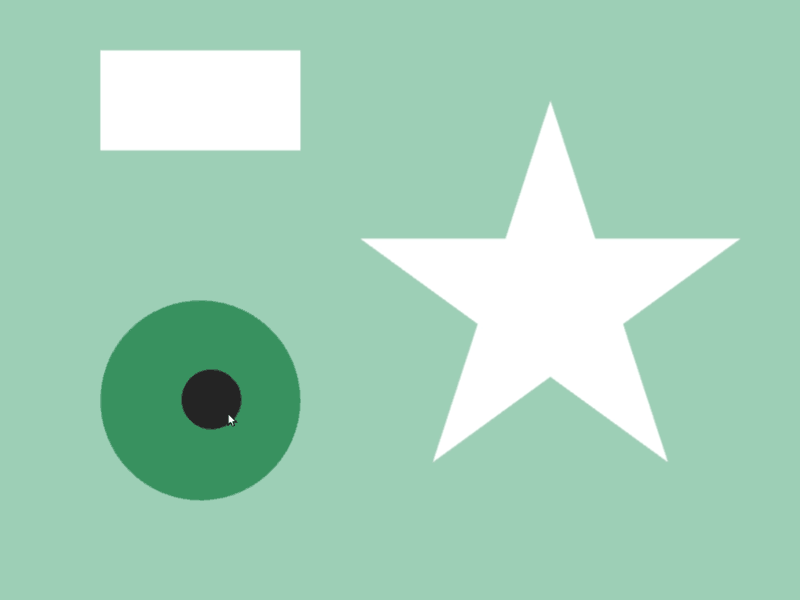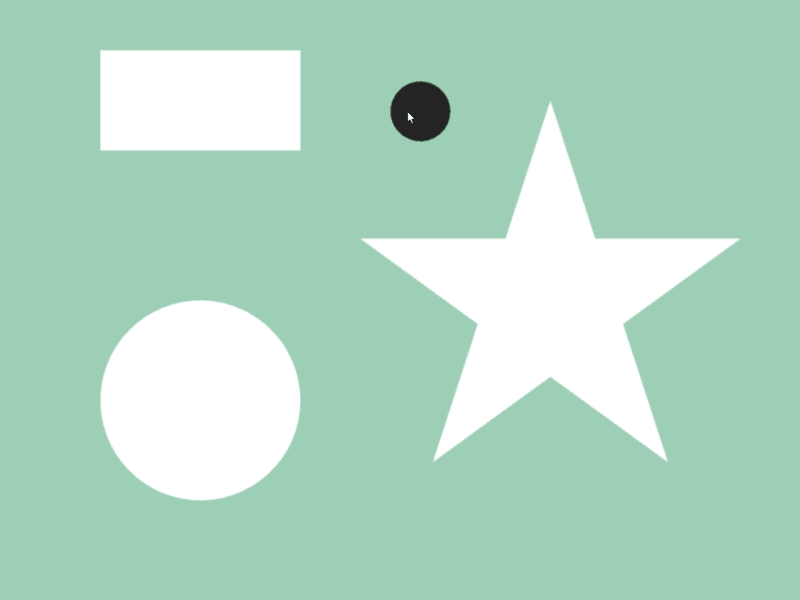
- In the following sample, when a circle that follows the mouse cursor overlaps with shapes like rectangles and stars, the color of those shapes changes
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 550, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Circle c{ Cursor::Pos(), 30 };
rect.draw(rect.intersects(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
circle.draw(circle.intersects(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
star.draw(star.intersects(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
c.draw(ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.4 Shape Contains¶
- Whether a shape
acompletely contains another shapebinside can be checked witha.contains(b) - Detection is possible between different shape classes
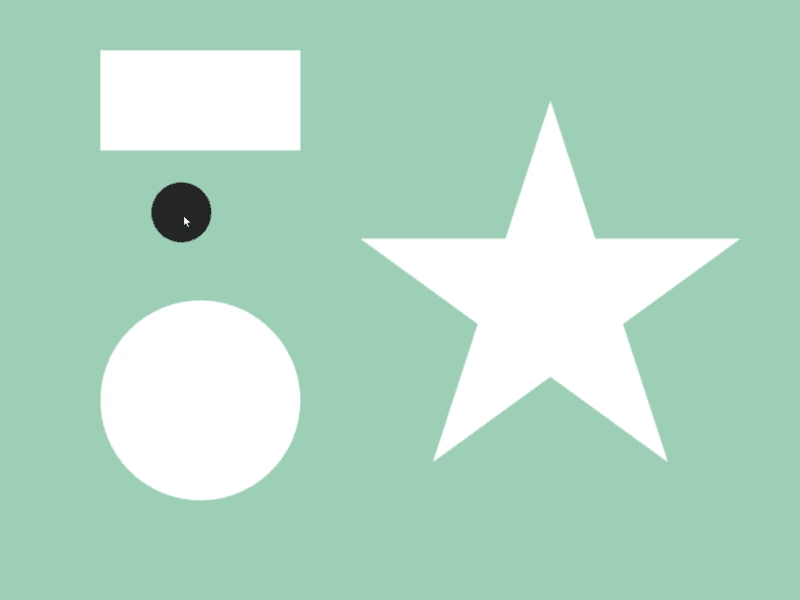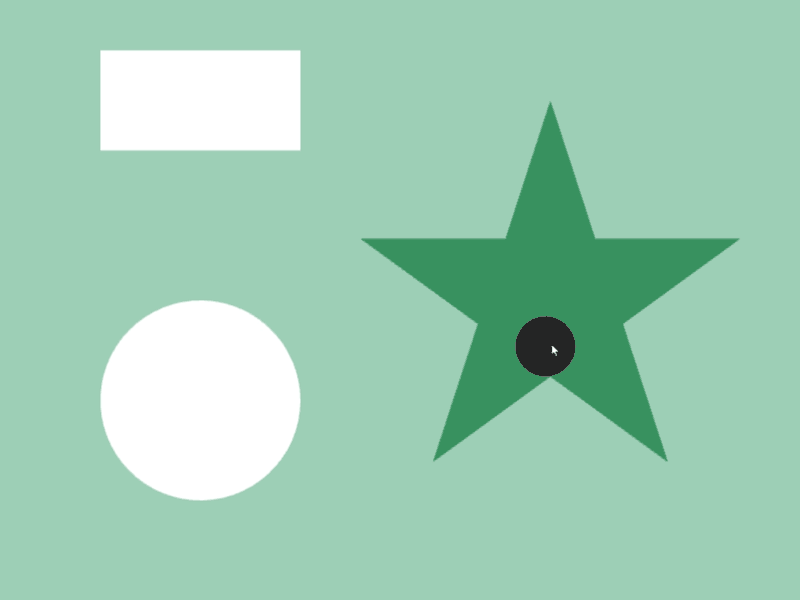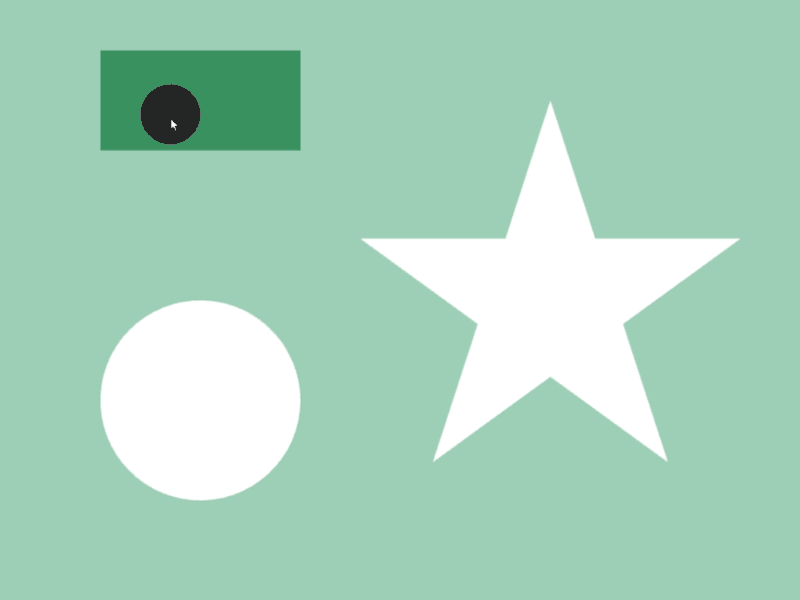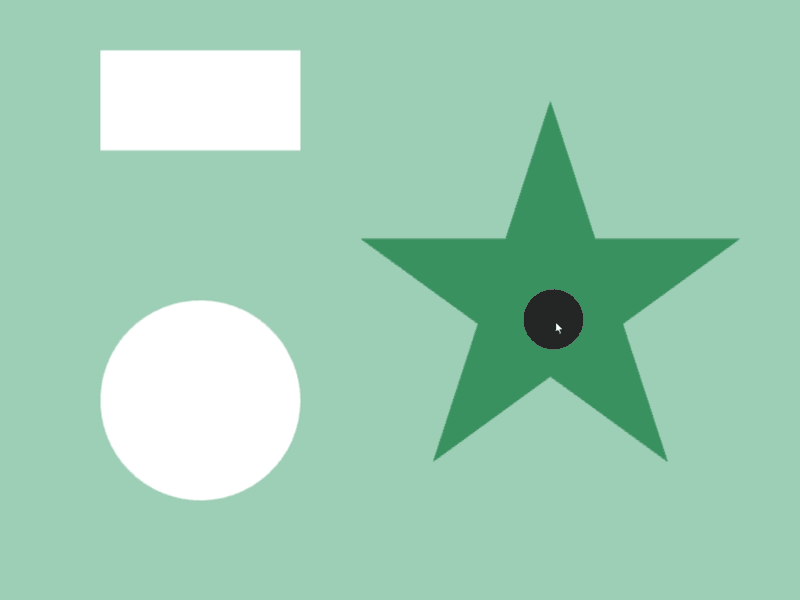
- In the following sample, when a circle that follows the mouse cursor is completely contained inside shapes like rectangles and stars, the color of those shapes changes
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 550, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Circle c{ Cursor::Pos(), 30 };
rect.draw(rect.contains(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
circle.draw(circle.contains(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
star.draw(star.contains(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
c.draw(ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.5 Getting Line Segment Intersection Position¶
- You can get intersection information of two line segments
aandbwitha.intersectsAt(b) - The return value of this function is
Optional<Vec2>, which becomes the following values depending on the intersection situation:
| Intersection Situation | Return Value |
|---|---|
| No intersection | none |
| Intersecting | Vec2{ coordinates of intersection point } |
| Parallel and overlapping | Vec2{ QNaN, QNaN } |
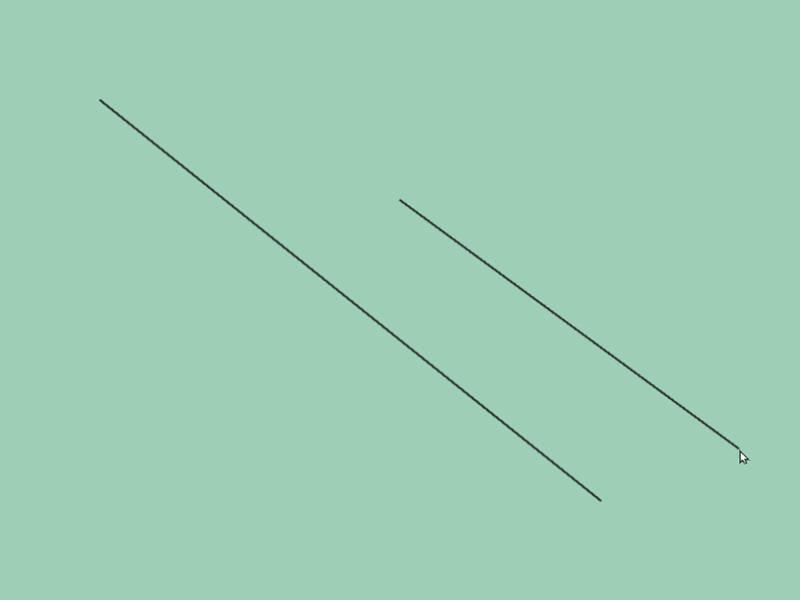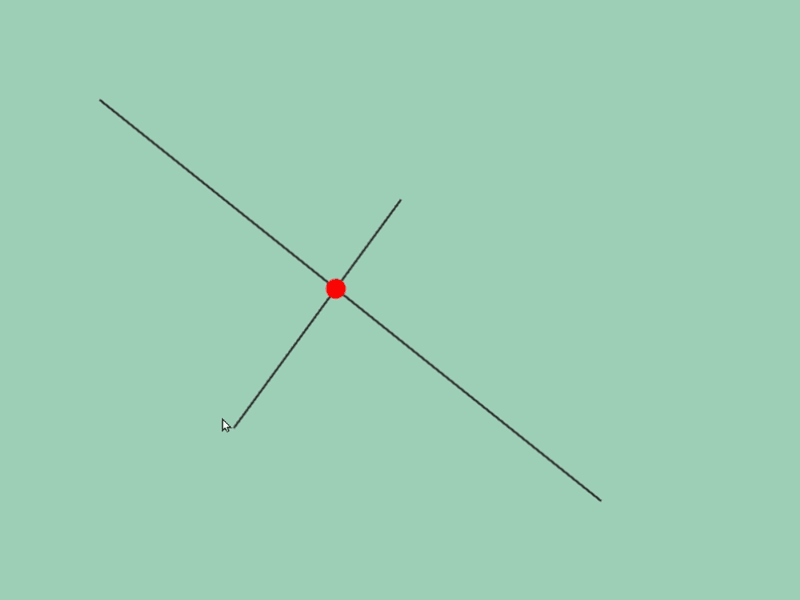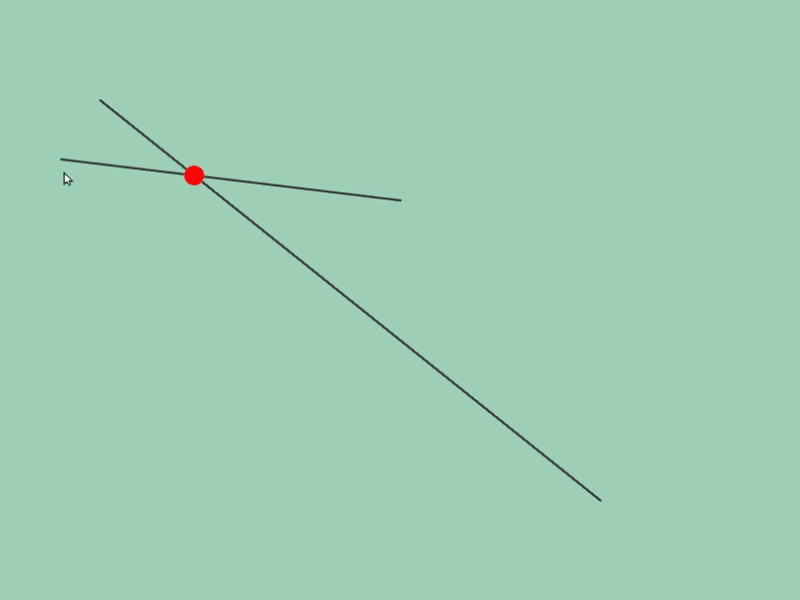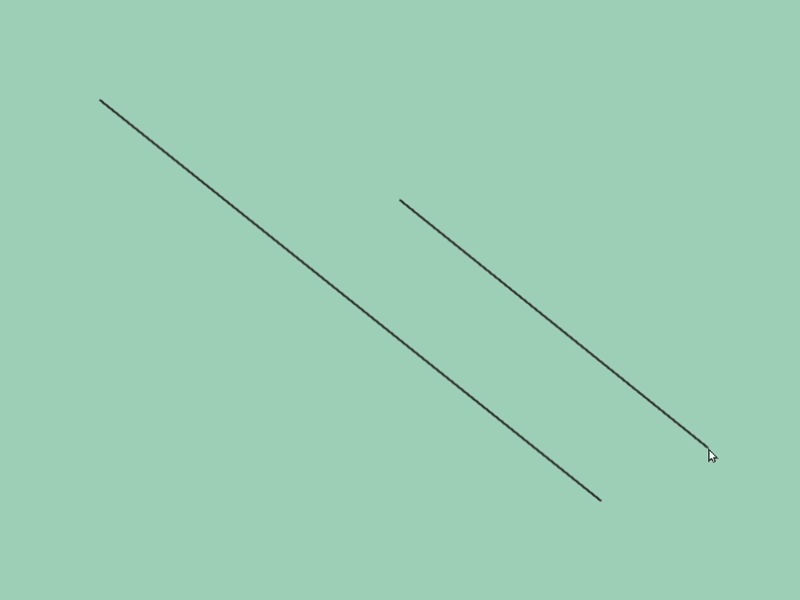
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Line line1{ 100, 100, 600, 500 };
while (System::Update())
{
const Line line2{ 400, 200, Cursor::Pos() };
line1.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
line2.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
if (const auto& intersection = line1.intersectsAt(line2))
{
Circle{ *intersection, 10 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
}
- You can check the case where two line segments are parallel and overlapping with the following code:
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
const Line line1{ 100, 100, 200, 200 };
const Line line2{ 100, 100, 300, 300 };
if (const auto intersection = line1.intersectsAt(line2))
{
Print << *intersection;
// If the intersection point is NaN, the two line segments are overlapping
if (intersection->hasNaN())
{
Print << U"Two lines are overlapped.";
}
}
while (System::Update())
{
}
}
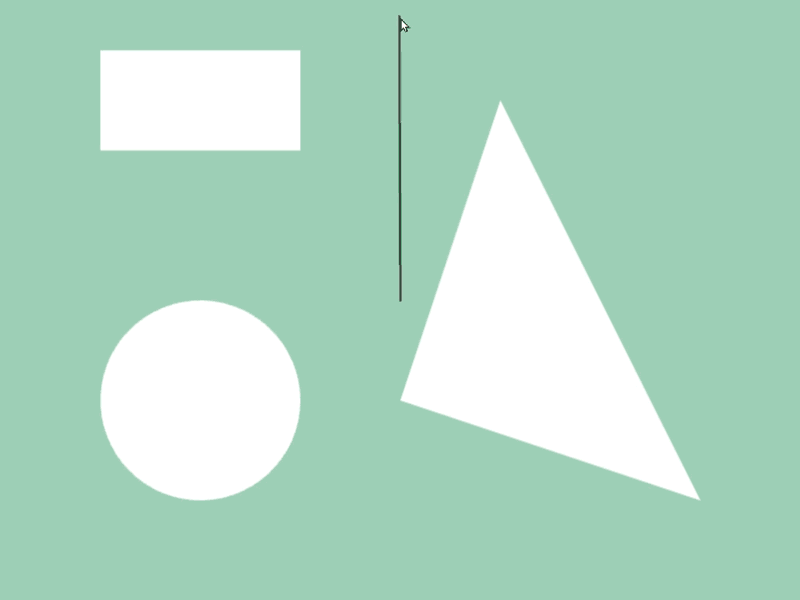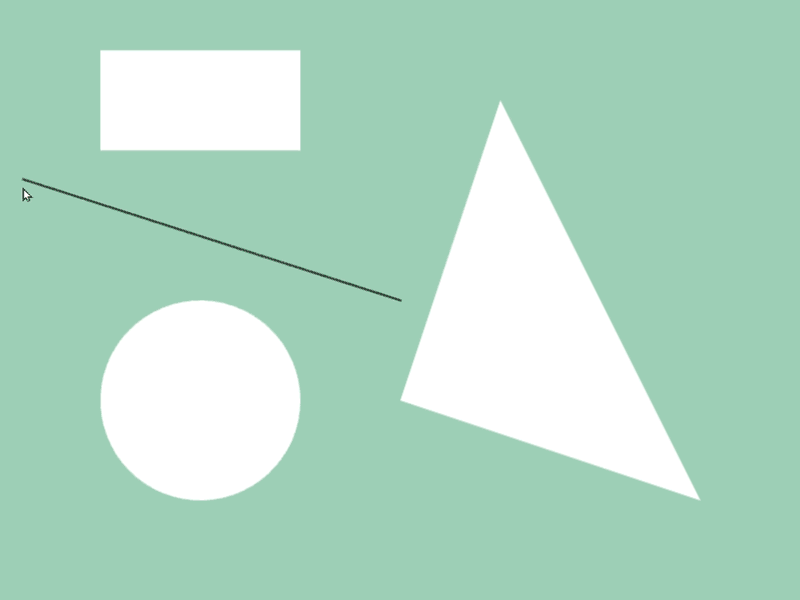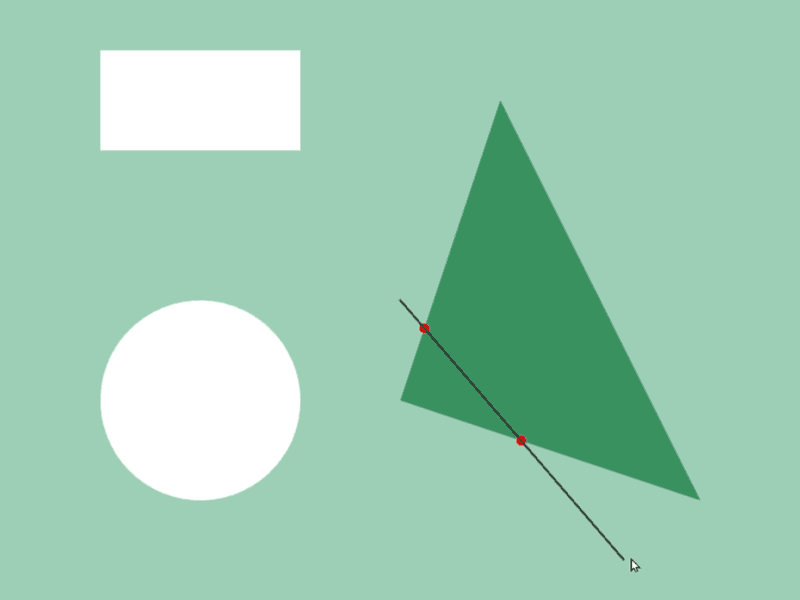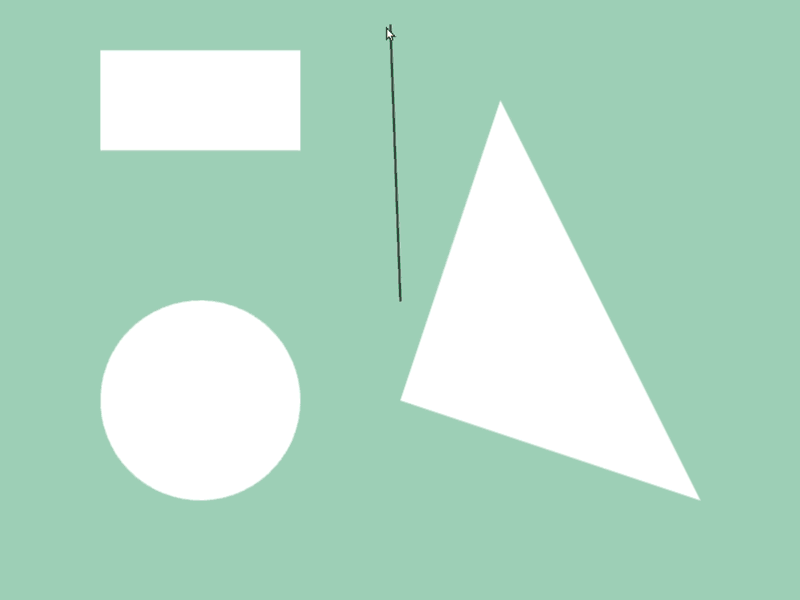
45.6 Getting Shape-to-Shape Intersection Position¶
- You can get intersection information of two shapes
aandbwitha.intersectsAt(b) - Detection is possible between different shape classes
- The return value of this function is
Optional<Array<Vec2>>, which becomes the following values depending on the intersection situation:
| Intersection Situation | Return Value |
|---|---|
| No intersection | none |
| Intersecting | Array<Vec2>{ coordinates of intersection points, ... } |
| Intersecting but intersection points could not be determined (cases like being contained inside) | Array<Vec2>{}(empty array) |
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Triangle triangle{ Vec2{ 500, 100 }, Vec2{ 700, 500 }, Vec2{ 400, 400 } };
while (System::Update())
{
const Line line{ 400, 300, Cursor::Pos() };
// Intersection information between rect and line
if (const auto points = rect.intersectsAt(line))
{
rect.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
// Display red circles at intersection coordinates
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 5 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // No intersection
{
rect.draw();
}
// Intersection information between circle and line
if (const auto points = circle.intersectsAt(line))
{
circle.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
// Display red circles at intersection coordinates
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 5 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // No intersection
{
circle.draw();
}
// Intersection information between triangle and line
if (const auto points = triangle.intersectsAt(line))
{
triangle.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
// Display red circles at intersection coordinates
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 5 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // No intersection
{
triangle.draw();
}
line.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.7 Getting Rectangle Overlap Area¶
- The overlapping area of two rectangles
aandbcan be obtained witha.getOverlap(b) - The return value of this function is
RectorRectF, and if there is no overlapping area, it returns an empty rectangle (rectangle with size 0) - Whether a rectangle
rectis empty can be determined withif (rect.isEmpty()),if (rect),if (not rect), etc.
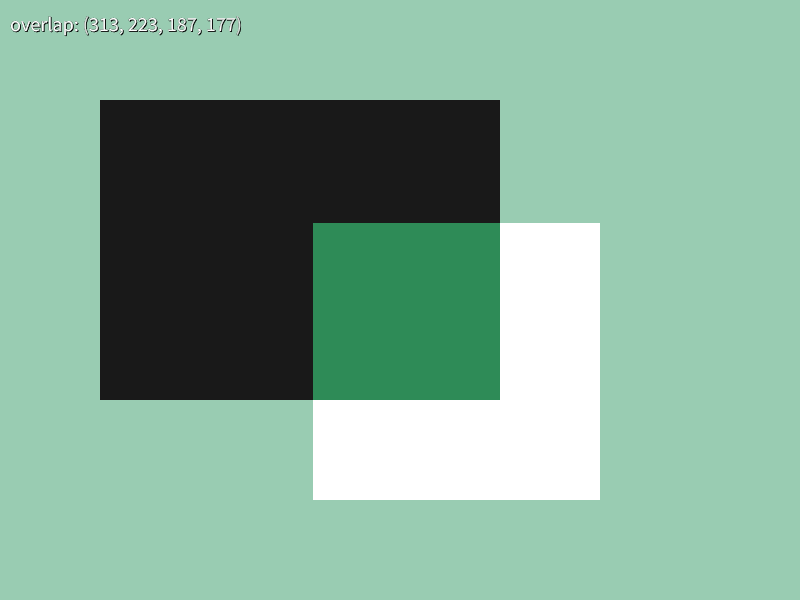
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect1{ 100, 100, 400, 300 };
while (System::Update())
{
ClearPrint();
const Rect rect2 = Rect::FromPoints(Cursor::Pos(), Point{ 600, 500 });
rect1.draw(ColorF{ 0.1 });
rect2.draw();
// Return overlapping area of two rectangles as Rect
if (const auto overlap = rect1.getOverlap(rect2))
{
Print << U"overlap: " << overlap;
overlap.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
}
}
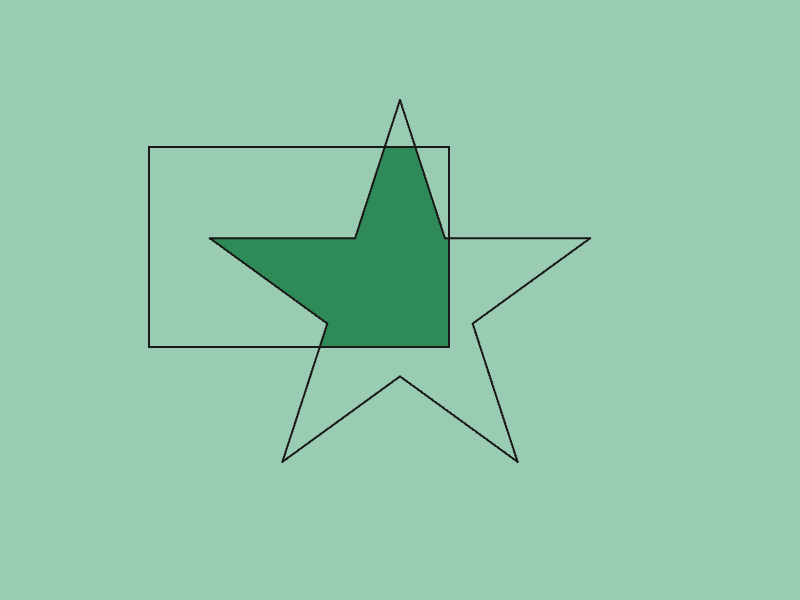
45.8 Polygon AND¶
- The intersection (common part) of two
Polygonsaandbcan be obtained withGeometry2D::And(a, b) - The return value is
Array<Polygon>, and if there is no common part, it returns an empty array
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 400, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Polygon rect = Rect{ Cursor::Pos(), 300, 200 }.asPolygon();
const Array<Polygon> polygons = Geometry2D::And(star, rect);
for (const auto& polygon : polygons)
{
polygon.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
star.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
rect.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
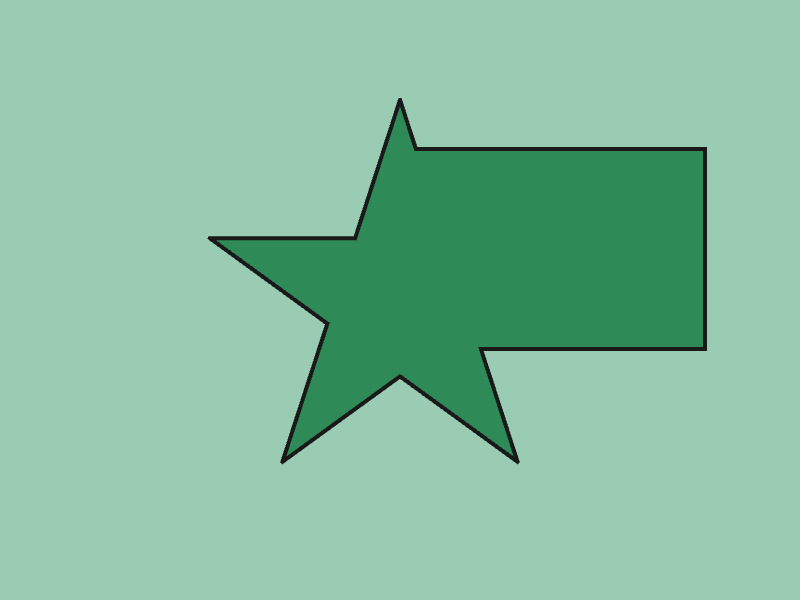
45.9 Polygon OR¶
- The union of two
Polygonsaandbcan be obtained withGeometry2D::Or(a, b) - The return value is
Array<Polygon>
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 400, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Polygon rect = Rect{ Cursor::Pos(), 300, 200 }.asPolygon();
const Array<Polygon> polygons = Geometry2D::Or(star, rect);
for (const auto& polygon : polygons)
{
polygon.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
polygon.drawFrame(4, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
}
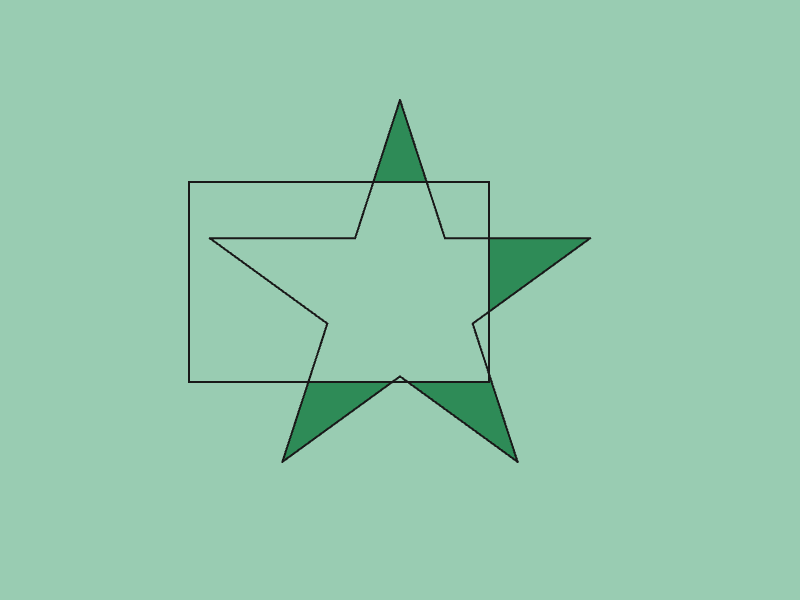
45.10 Polygon Difference¶
- The difference of two
Polygonsaandb(removing the part ofathat overlaps withb) can be obtained withGeometry2D::Subtract(a, b) - The return value is
Array<Polygon>
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 400, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Polygon rect = Rect{ Cursor::Pos(), 300, 200 }.asPolygon();
const Array<Polygon> polygons = Geometry2D::Subtract(star, rect);
for (const auto& polygon : polygons)
{
polygon.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
star.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
rect.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.11 Polygon Convex Hull¶
- The
Polygonclass has a member function.computeConvexHull()that finds the convex hull (smallest convex polygon that completely encloses all vertices) of itself - The return value is
Polygon