電卓アプリを作る¶
| 難易度 | 入門 | 時間 | 30 分~ |
1. 背景色を設定する¶

Scene::SetBackground(色);を使って背景色を設定します。
コード
2. ボタンの情報を用意する¶

- ボタンの領域を表す
Rectと、ボタンに書かれるテキストを表すStringを持つクラスButtonを作成します。 - 「1」ボタンの情報を
Buttonクラスの変数buttonの初期値として設定します。
コード
3. ボタンの背景を描く¶
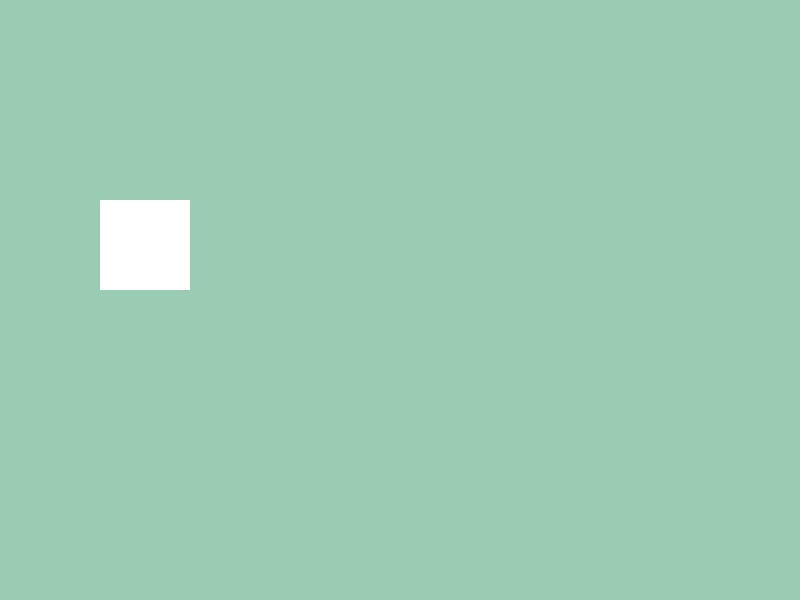

Buttonクラスのメンバ変数.rectにアクセスし、ボタンの背景を描画します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタンの情報
Button button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
while (System::Update())
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.draw();
}
}
4. ボタンの角を丸くする¶

Rectのメンバ関数.rounded(角の半径)を使って、ボタンの角を丸くします。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタンの情報
Button button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
while (System::Update())
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw();
}
}
5. ボタンに文字を表示する¶

- テキストを表示するための
Fontを用意します。 Buttonのメンバ変数.textにアクセスし、ボタンのテキストを描画します。
新しい機能
- font(テキスト).drawAt(フォントサイズ, 位置, 色);` は、指定した位置が中心となるようにテキストを描画します。
Rectの.center()メンバ関数は、長方形の中心の座標を返します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタン用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 40, Typeface::Bold };
// ボタンの情報
Button button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
while (System::Update())
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw();
// ボタンのテキストを描画する
font(button.text).drawAt(32, button.rect.center(), ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
6. ボタンの上でマウスカーソルを手の形にする¶

Rectのメンバ関数.mouseOver()で、マウスカーソルがボタンの上にあるかを判定します。Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);で、現在のマウスカーソルのスタイルを手の形に変更します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタン用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 40, Typeface::Bold };
// ボタンの情報
Button button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
while (System::Update())
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw();
// ボタンのテキストを描画する
font(button.text).drawAt(32, button.rect.center(), ColorF{ 0.1 });
// マウスがボタンの上にあるとき
if (button.rect.mouseOver())
{
// マウスカーソルを手の形にする
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
}
}
7. ボタンで数式を入力する¶

- 電卓への入力式を文字列で管理する
String型の変数expressionを用意します。 - ボタンがクリックされたときに、ボタンのテキスト「U"1"」を
expressionに追加します。 Printを使って、入力式の内容を簡易表示します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタン用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 40, Typeface::Bold };
// ボタンの情報
Button button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
// 入力式
String expression;
while (System::Update())
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw();
// ボタンのテキストを描画する
font(button.text).drawAt(32, button.rect.center(), ColorF{ 0.1 });
// マウスがボタンの上にあるとき
if (button.rect.mouseOver())
{
// マウスカーソルを手の形にする
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
// ボタンがクリックされたとき
if (button.rect.leftClicked())
{
// 数式にボタンのテキストを追加する
expression += button.text;
}
ClearPrint();
Print << expression; // 数式を簡易表示する
}
}
8. ボタンを増やす¶
- 配列
Array<Button>を使って、より多くのボタンを管理します。 for (const auto& button : buttons) { }内に、各ボタンに対する処理を記述します。- ボタンがクリックされた場合は、そのボタンのテキストに応じて、入力式
expressionを更新します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタン用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 40, Typeface::Bold };
// ボタンの情報の配列
Array<Button> buttons;
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 200, 200, 90, 90 }, U"2" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 300, 200, 90, 90 }, U"3" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 200, 90, 90 }, U"+" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 300, 90, 90 }, U"=" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 400, 90, 90 }, U"C" };
// 入力式
String expression;
while (System::Update())
{
// 各ボタンについて
for (const auto& button : buttons)
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw();
// ボタンのテキストを描画する
font(button.text).drawAt(32, button.rect.center(), ColorF{ 0.1 });
// マウスがボタンの上にあるとき
if (button.rect.mouseOver())
{
// マウスカーソルを手の形にする
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
// ボタンがクリックされたとき
if (button.rect.leftClicked())
{
if (button.text == U"=")
{
// ToDo
}
else if (button.text == U"+")
{
expression += button.text;
}
else if (button.text == U"C")
{
// 数式を消去する
expression.clear();
}
else
{
// 数式にボタンのテキストを追加する
expression += button.text;
}
}
}
ClearPrint();
Print << expression; // 数式を簡易表示する
}
}
9. 数式の表示エリアを追加する¶
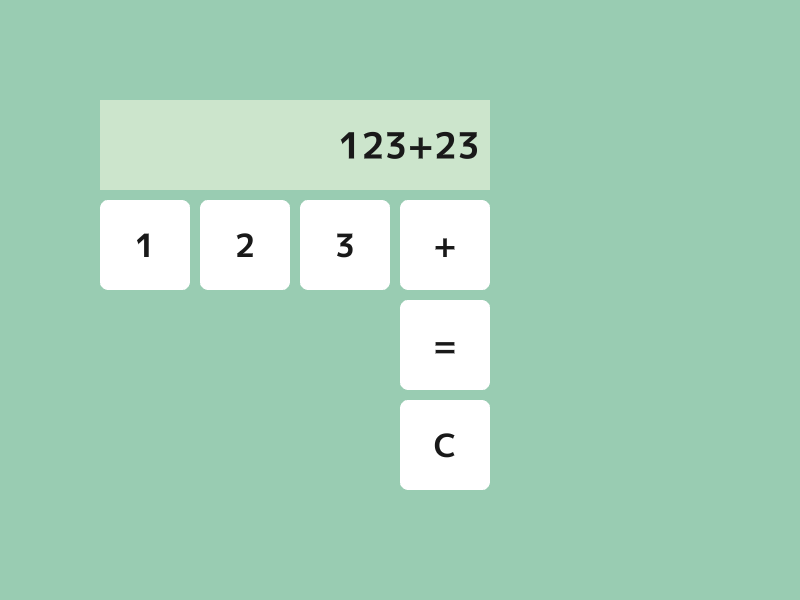
- 電卓に数式を表示するエリアを追加します。
- 表示エリアから 10 ピクセル左にずらして、数式を右寄せで表示します。
新しい機能
font(テキスト).draw(フォントサイズ, Arg::rightCenter = 位置, 色);は、指定した位置がテキストの右辺の中心となるよう、右寄せしてテキストを描画します。Rectの.rightCenter()メンバ関数は、長方形の右辺の中心の座標を返します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタン用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 40, Typeface::Bold };
// 結果表示エリアの色
const ColorF displayColor{ 0.8, 0.9, 0.8 };
// 結果表示エリアのテキストの色
const ColorF displayTextColor{ 0.1 };
// 結果表示エリアの長方形
const Rect displayRect{ 100, 100, 390, 90 };
// ボタンの情報の配列
Array<Button> buttons;
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 200, 200, 90, 90 }, U"2" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 300, 200, 90, 90 }, U"3" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 200, 90, 90 }, U"+" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 300, 90, 90 }, U"=" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 400, 90, 90 }, U"C" };
// 入力式
String expression;
while (System::Update())
{
// 各ボタンについて
for (const auto& button : buttons)
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw();
// ボタンのテキストを描画する
font(button.text).drawAt(32, button.rect.center(), ColorF{ 0.1 });
// マウスがボタンの上にあるとき
if (button.rect.mouseOver())
{
// マウスカーソルを手の形にする
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
// ボタンがクリックされたとき
if (button.rect.leftClicked())
{
if (button.text == U"=")
{
// ToDo
}
else if (button.text == U"+")
{
expression += button.text;
}
else if (button.text == U"C")
{
// 数式を消去する
expression.clear();
}
else
{
// 数式にボタンのテキストを追加する
expression += button.text;
}
}
}
// 結果表示エリアを描画する
displayRect.draw(displayColor);
// 結果表示エリアに数式を描画する
font(expression).draw(36, Arg::rightCenter = (displayRect.rightCenter() + Vec2{ -10, 0 }), displayTextColor);
}
}
10. 計算処理を追加する¶
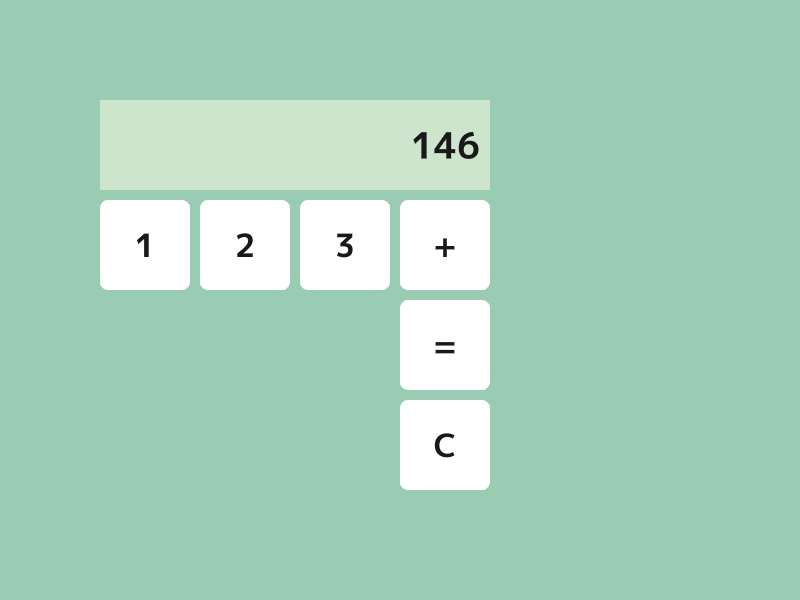
- 「=」ボタンを押したときに入力式を計算して、その結果を新しい入力式とするための関数
PushEqualを実装します。 - 「+」ボタンを押したときに入力式に「+」を追加するための関数
PushPlusを実装します。
新しい機能
!(ノット)はbool型の値を反転します。String型の変数の.isEmpty()メンバ関数は、文字列が空かどうかを判定します。String型の変数の.back()メンバ関数は、文字列の末尾の文字を返します。空の場合はエラーになります。IsDigit(char32 ch)関数は、引数の文字chが数字であるかを判定します。Eval(String expression)関数は、数式expressionを評価した結果をdouble型で返します。数式が不正な場合はNaNを返します。NaNであるかはIsNaN(double x)関数で判定できます。
Format(double x)関数は、double型の値xをStringに変換して返します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
};
/// @brief 数式が数字で終わるかを返します。
/// @param expression 数式
/// @return 数字で終わる場合 true, それ以外の場合 false
bool EndsWithDigit(String expression)
{
if (expression.isEmpty())
{
return false;
}
return IsDigit(expression.back());
}
/// @brief = ボタンが押されたときの処理を行います。
/// @param expression 現在の数式
/// @return 新しい数式
String PushEqual(String expression)
{
// 数字で終わっていない場合は何もしない
if (!EndsWithDigit(expression))
{
return expression;
}
// 数式パーサで数式を評価する
double result = Eval(expression);
// 評価結果を文字列に変換して返す
return Format(result);
}
/// @brief + ボタンが押されたときの処理を行います。
/// @param expression 現在の数式
/// @return 新しい数式
String PushPlus(String expression)
{
// 数字で終わっていない場合は何もしない
if (!EndsWithDigit(expression))
{
return expression;
}
// 数式の末尾に + を追加して返す
return (expression + U"+");
}
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタン用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 40, Typeface::Bold };
// 結果表示エリアの色
const ColorF displayColor{ 0.8, 0.9, 0.8 };
// 結果表示エリアのテキストの色
const ColorF displayTextColor{ 0.1 };
// 結果表示エリアの長方形
const Rect displayRect{ 100, 100, 390, 90 };
// ボタンの情報の配列
Array<Button> buttons;
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 200, 200, 90, 90 }, U"2" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 300, 200, 90, 90 }, U"3" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 200, 90, 90 }, U"+" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 300, 90, 90 }, U"=" };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 400, 90, 90 }, U"C" };
// 入力式
String expression;
while (System::Update())
{
// 各ボタンについて
for (const auto& button : buttons)
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw();
// ボタンのテキストを描画する
font(button.text).drawAt(32, button.rect.center(), ColorF{ 0.1 });
// マウスがボタンの上にあるとき
if (button.rect.mouseOver())
{
// マウスカーソルを手の形にする
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
// ボタンがクリックされたとき
if (button.rect.leftClicked())
{
if (button.text == U"=")
{
expression = PushEqual(expression);
}
else if (button.text == U"+")
{
expression = PushPlus(expression);
}
else if (button.text == U"C")
{
// 数式を消去する
expression.clear();
}
else
{
// 数式にボタンのテキストを追加する
expression += button.text;
}
}
}
// 結果表示エリアを描画する
displayRect.draw(displayColor);
// 結果表示エリアに数式を描画する
font(expression).draw(36, Arg::rightCenter = (displayRect.rightCenter() + Vec2{ -10, 0 }), displayTextColor);
}
}
11. ボタンのスタイルをカスタマイズする¶
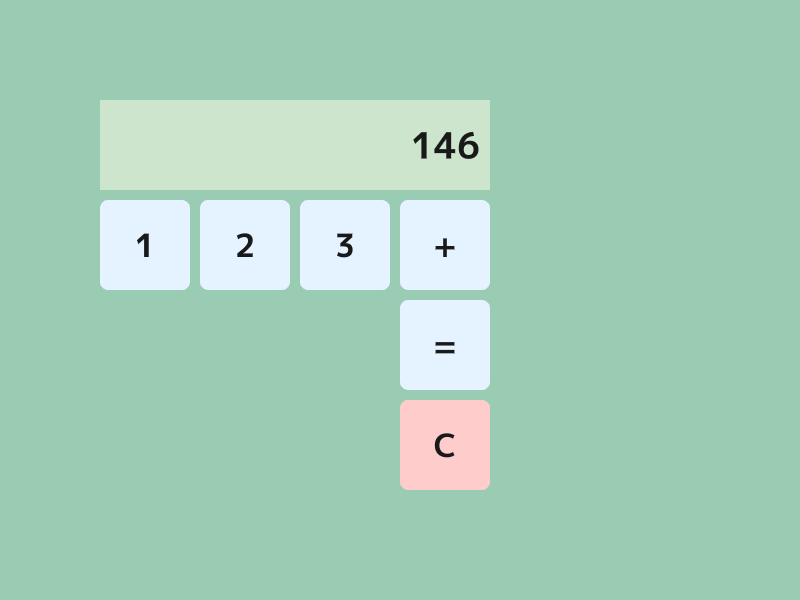
Buttonクラスに、ボタンの背景色とテキストの色を表すColorF型のメンバ変数を追加します。
コード
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
/// @brief ボタンクラス
struct Button
{
/// @brief ボタンの長方形
Rect rect;
/// @brief ボタンのテキスト
String text;
/// @brief ボタンの色
ColorF backgroundColor;
/// @brief テキストの色
ColorF textColor;
};
/// @brief 数式が数字で終わるかを返します。
/// @param expression 数式
/// @return 数字で終わる場合 true, それ以外の場合 false
bool EndsWithDigit(String expression)
{
if (expression.isEmpty())
{
return false;
}
return IsDigit(expression.back());
}
/// @brief = ボタンが押されたときの処理を行います。
/// @param expression 現在の数式
/// @return 新しい数式
String PushEqual(String expression)
{
// 数字で終わっていない場合は何もしない
if (!EndsWithDigit(expression))
{
return expression;
}
// 数式パーサで数式を評価する
double result = Eval(expression);
// 評価結果を文字列に変換して返す
return Format(result);
}
/// @brief + ボタンが押されたときの処理を行います。
/// @param expression 現在の数式
/// @return 新しい数式
String PushPlus(String expression)
{
// 数字で終わっていない場合は何もしない
if (!EndsWithDigit(expression))
{
return expression;
}
// 数式の末尾に + を追加して返す
return (expression + U"+");
}
void Main()
{
// 背景の色を設定する
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
// ボタン用のフォント
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 40, Typeface::Bold };
// 数字ボタンの色
const ColorF numberButtonColor{ 0.9, 0.95, 1.0 };
// クリアボタンの色
const ColorF clearButtonColor{ 1.0, 0.8, 0.8 };
// ボタンのテキストの色
const ColorF buttonTextColor{ 0.1 };
// 結果表示エリアの色
const ColorF displayColor{ 0.8, 0.9, 0.8 };
// 結果表示エリアのテキストの色
const ColorF displayTextColor{ 0.1 };
// 結果表示エリアの長方形
const Rect displayRect{ 100, 100, 390, 90 };
// ボタンの情報の配列
Array<Button> buttons;
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 100, 200, 90, 90 }, U"1", numberButtonColor, buttonTextColor };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 200, 200, 90, 90 }, U"2", numberButtonColor, buttonTextColor };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 300, 200, 90, 90 }, U"3", numberButtonColor, buttonTextColor };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 200, 90, 90 }, U"+", numberButtonColor, buttonTextColor };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 300, 90, 90 }, U"=", numberButtonColor, buttonTextColor };
buttons << Button{ Rect{ 400, 400, 90, 90 }, U"C", clearButtonColor, buttonTextColor };
// 入力式
String expression;
while (System::Update())
{
// 各ボタンについて
for (const auto& button : buttons)
{
// ボタンの背景を描画する
button.rect.rounded(8).draw(button.backgroundColor);
// ボタンのテキストを描画する
font(button.text).drawAt(32, button.rect.center(), button.textColor);
// マウスがボタンの上にあるとき
if (button.rect.mouseOver())
{
// マウスカーソルを手の形にする
Cursor::RequestStyle(CursorStyle::Hand);
}
// ボタンがクリックされたとき
if (button.rect.leftClicked())
{
if (button.text == U"=")
{
expression = PushEqual(expression);
}
else if (button.text == U"+")
{
expression = PushPlus(expression);
}
else if (button.text == U"C")
{
// 数式を消去する
expression.clear();
}
else
{
// 数式にボタンのテキストを追加する
expression += button.text;
}
}
}
// 結果表示エリアを描画する
displayRect.draw(displayColor);
// 結果表示エリアに数式を描画する
font(expression).draw(36, Arg::rightCenter = (displayRect.rightCenter() + Vec2{ -10, 0 }), displayTextColor);
}
}
発展¶
ここから先は、自分で考えてプログラムを改良してみましょう。
機能のアイデア¶
- 残りの数字を追加する
- 引き算、掛け算、割り算を追加する
Eval()は-や*,/にも対応しています。
- 括弧を入力できるようにする
- バックスペース(1 文字削除)ボタンを追加する
Stringのメンバ関数.pop_back()は、文字列の末尾の文字を削除します。文字列が空の場合はエラーになります。
- 小数を含む数を入力できるようにする
- キーボードで数字を入力できるようにする
- 平方根を計算できるようにする
Eval()はsqrt(25)のような数式にも対応しています。
- 以前の計算結果を記録して再利用できるようにする
- 表示エリアをクリックすると、その数式をクリップボードにコピーする
Clipboard::SetText(s);は、文字列sをクリップボードにコピーします。
デザインのアイデア¶
- ボタンのサイズや配置をアレンジする
- マウスオーバーでボタンの色を変える