24. あたり判定¶
図形の交差判定を行う方法を学びます。
24.1 マウスオーバー¶
ある図形 shape の領域にマウスカーソルが重なっているかを、shape.mouseOver() で調べられます。
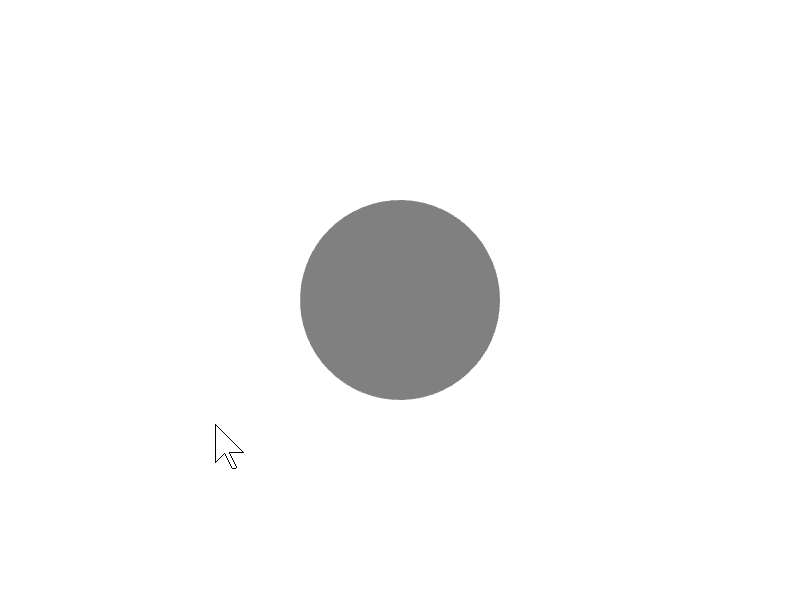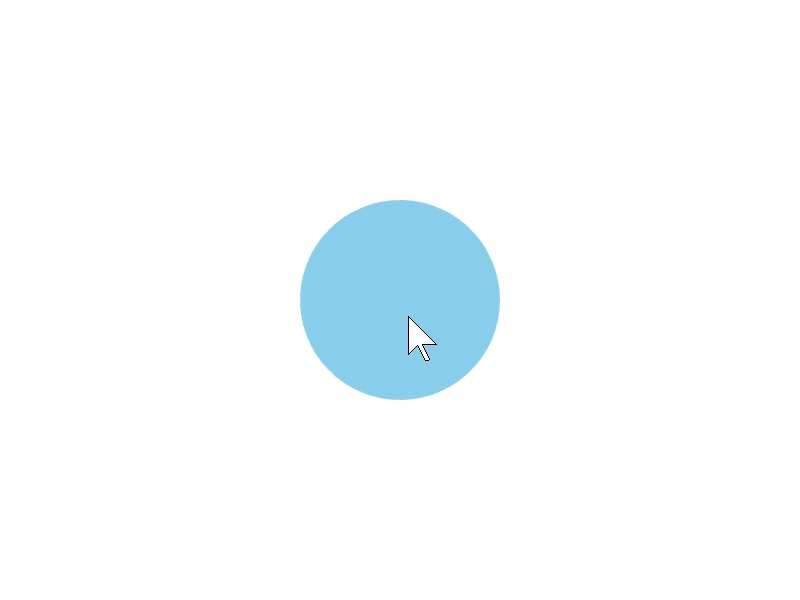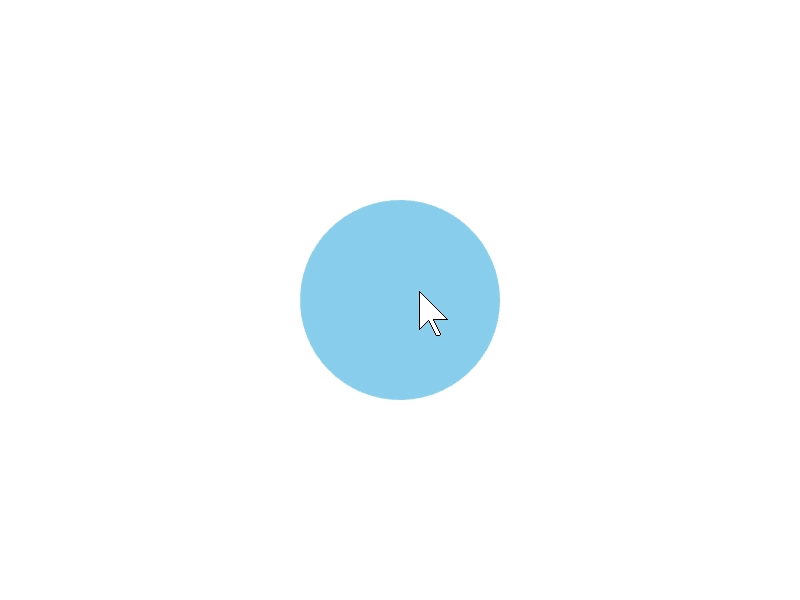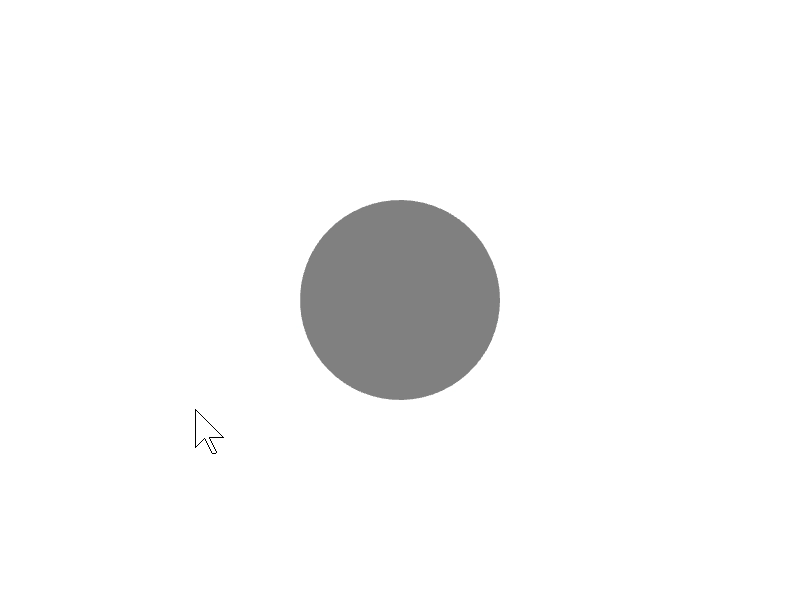
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Circle circle{ Scene::Center(), 100 };
while (System::Update())
{
if (circle.mouseOver())
{
// 円にマウスカーソルが重なっていれば水色
circle.draw(Palette::Skyblue);
}
else
{
// 重なっていなければ灰色
circle.draw(Palette::Gray);
}
}
}
条件演算子を使って短く書くこともできます。
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Circle circle{ Scene::Center(), 100 };
while (System::Update())
{
// 円にマウスカーソルが重なっていれば水色、そうでなければ灰色
circle.draw(circle.mouseOver() ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
}
}
24.2 図形のクリック¶
ある図形 shape が左クリックされたかを、shape.leftClicked() で調べられます。.leftClicked() は、最初に押し込んだフレームのみ true を返します。図形を押し続けていてもそれ以降は false を返します。
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Circle circle{ Scene::Center(), 100 };
int32 count = 0;
while (System::Update())
{
ClearPrint();
Print << count;
// 円が左クリックされたら
if (circle.leftClicked())
{
++count;
}
circle.draw(Palette::Gray);
}
}
24.3 図形が押されている¶
ある図形 shape が左クリックされているかを、shape.leftPressed() で調べられます。.leftPressed() は、最初に押し込んだフレームだけでなく、それ以降押され続けている場合にも true を返します。
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Circle circle{ Scene::Center(), 100 };
while (System::Update())
{
// 円が押されていれば水色、そうでなければ灰色
circle.draw(circle.leftPressed() ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
}
}
24.4 図形の交差¶
2 つの図形 a と b が交差しているかは、a.intersects(b) で調べられます。異なる図形クラスの間でも交差判定が可能です。

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 550, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Circle c{ Cursor::Pos(), 30 };
rect.draw(rect.intersects(c) ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
circle.draw(circle.intersects(c) ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
star.draw(star.intersects(c) ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
c.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
}
24.5 図形を内側に含む¶
ある図形 a が別の図形 b を完全に内側に含んでいるかは、a.contains(b) で調べられます。
次のサンプルでは、マウスカーソルに追従する円が、長方形や星などの図形の内部に完全に含まれているときに、その図形の色を変更します。
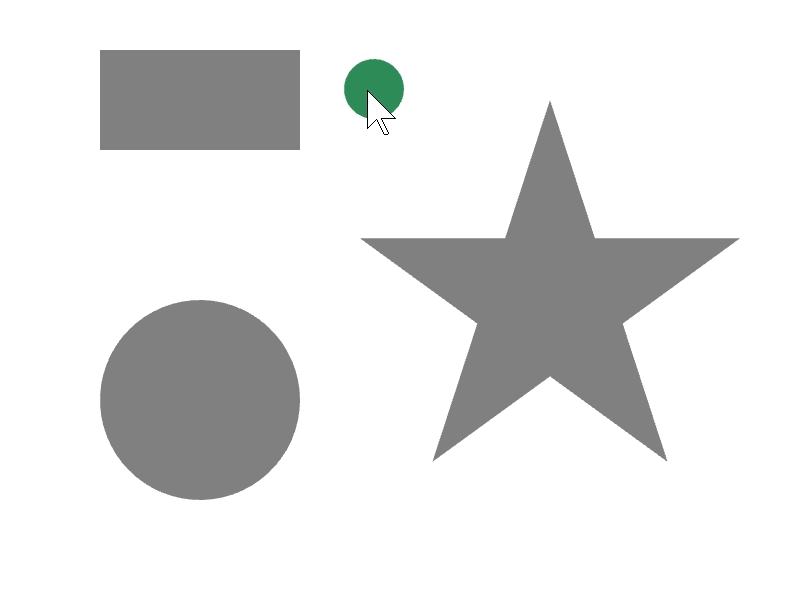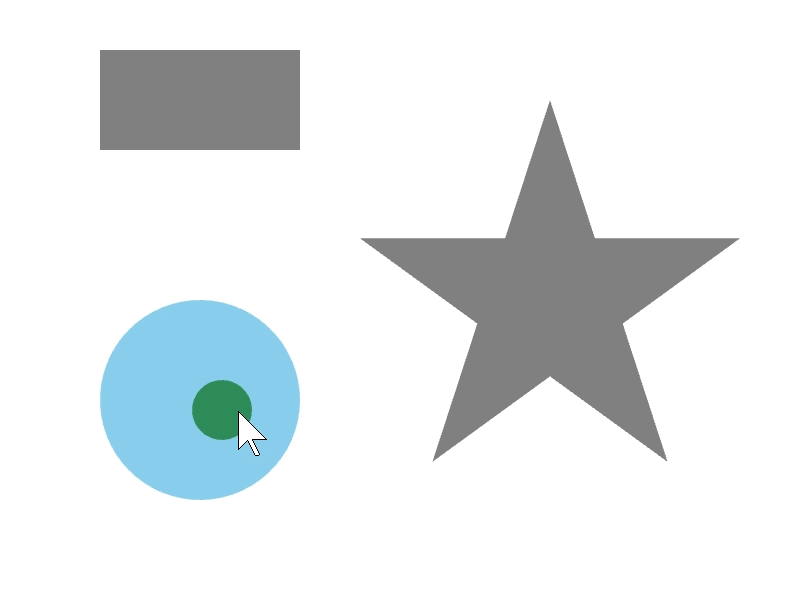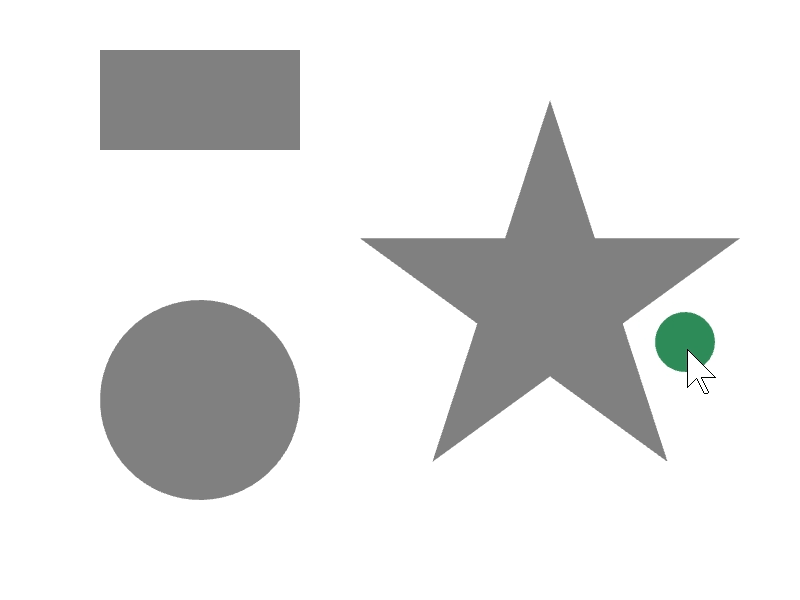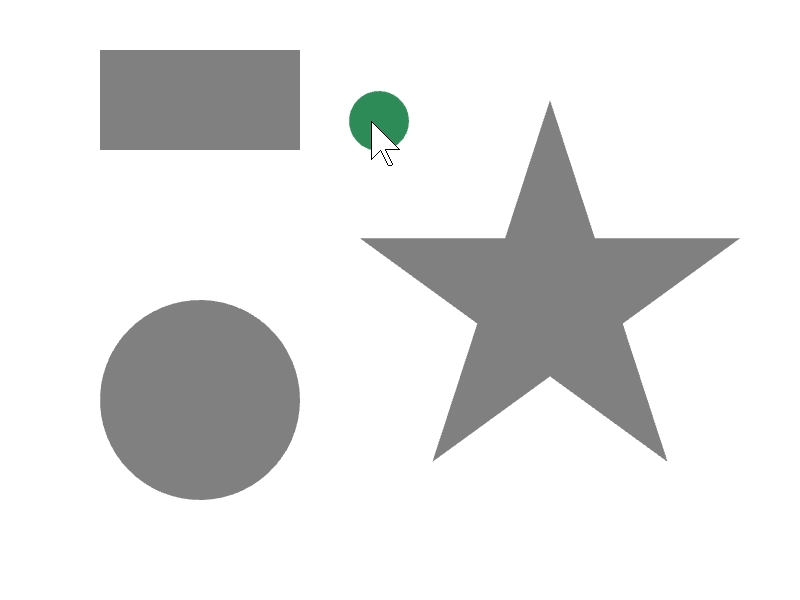
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 550, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Circle c{ Cursor::Pos(), 30 };
rect.draw(rect.contains(c) ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
circle.draw(circle.contains(c) ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
star.draw(star.contains(c) ? Palette::Skyblue : Palette::Gray);
c.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
}
24.6 線分どうしの交差位置を取得する¶
2 つの線分 a, b の交差情報を a.intersectsAt(b) で取得できます。この関数の戻り値は Optional<Vec2> で、交差の状況に応じて次のような値になります。
| 交差の状況 | 戻り値 |
|---|---|
| 交差していない | none |
| 交差している | Vec2{ 交点の座標 } |
| 重なっている | Vec2{ QNaN, QNaN } |
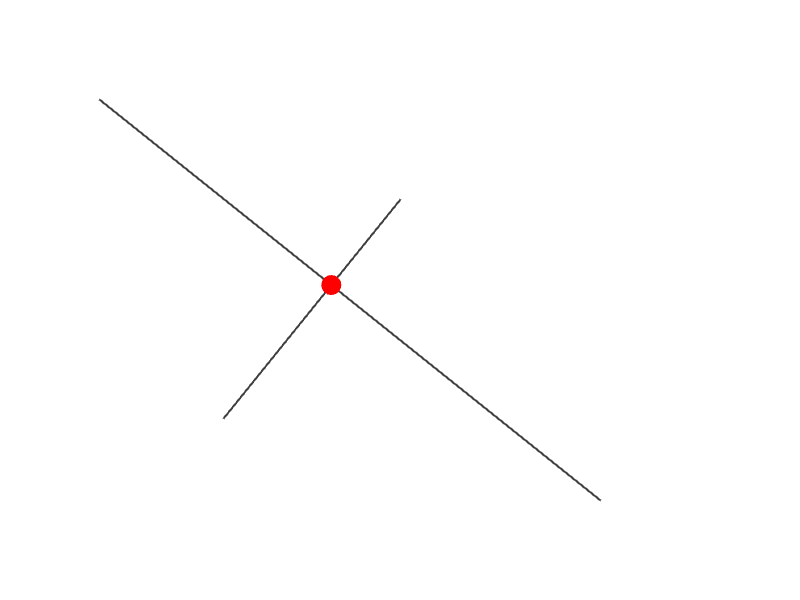
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Line line1{ 100, 100, 600, 500 };
while (System::Update())
{
const Line line2{ 400, 200, Cursor::Pos() };
line1.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.25 });
line2.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.25 });
if (const auto& intersection = line1.intersectsAt(line2))
{
Circle{ *intersection, 10 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
}
次のコードで、2 つの線分が重なっているときの結果を確認できます。

# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
const Line line1{ 100, 100, 200, 200 };
const Line line2{ 100, 100, 300, 300 };
if (const auto intersection = line1.intersectsAt(line2))
{
Print << *intersection;
// 交点が NaN なら、2 つの線分は重なっている
if (intersection->hasNaN())
{
Print << U"Two lines are overlapped.";
}
}
while (System::Update())
{
}
}
24.7 線分と図形の交差位置を取得する¶
ある図形 a と b の辺の交差情報を a.intersectsAt(b) で取得できます。この関数の戻り値は Optional<Array<Vec2>> で、交差の状況に応じて次のような値になります。2 つの線分がオーバーラップする場合に空の配列を返すことがあります。
| 交差の状況 | 戻り値 |
|---|---|
| 交差していない | none |
| 交差している | Array<Vec2>{ 交点の座標, ... } |
| 交差しているが交点を求められなかった | Array<Vec2>{}(空の配列) |
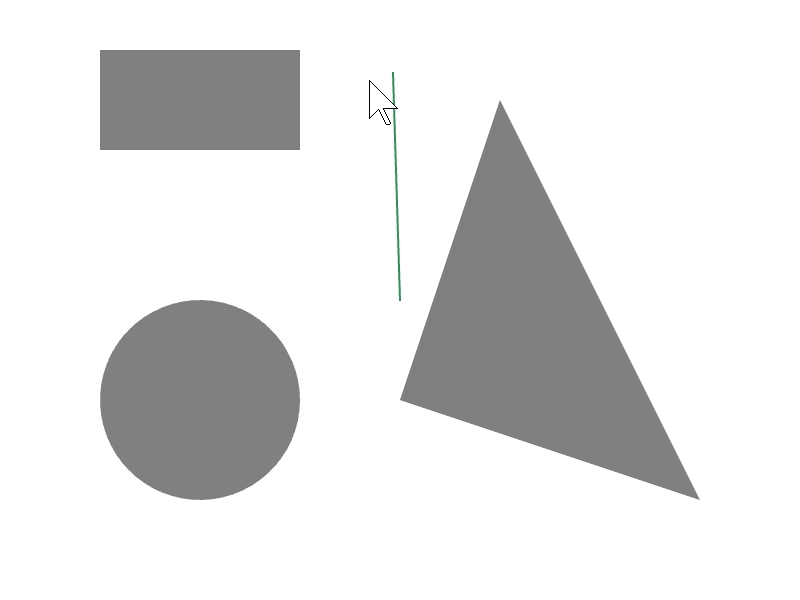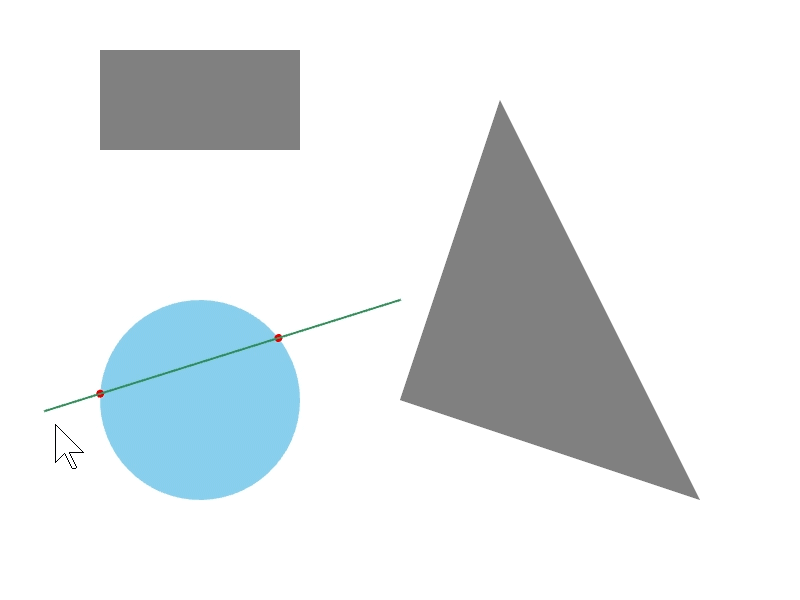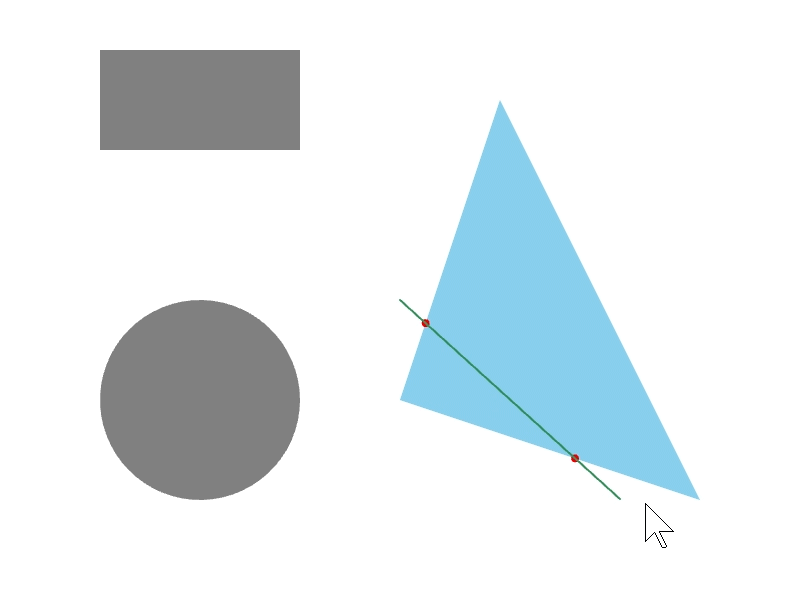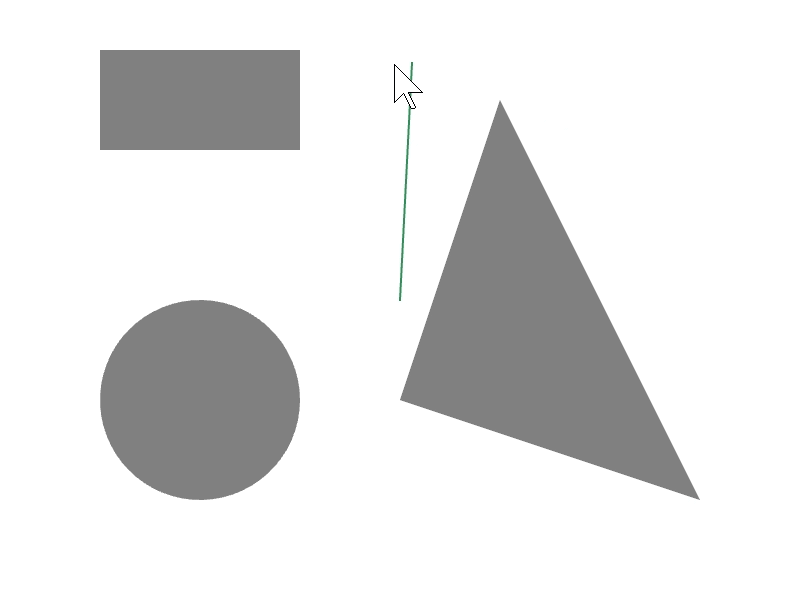
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Triangle triangle{ Vec2{ 500, 100 }, Vec2{ 700, 500 }, Vec2{ 400, 400 } };
while (System::Update())
{
const Line line{ Scene::Center(), Cursor::Pos() };
// rect と line の交差情報を取得する
if (const auto points = rect.intersectsAt(line))
{
rect.draw(Palette::Skyblue);
// 交差する座標に赤い円を表示する
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 4 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // 交差しない
{
rect.draw(Palette::Gray);
}
// circle と line の交差情報を取得
if (const auto points = circle.intersectsAt(line))
{
circle.draw(Palette::Skyblue);
// 交差する座標に赤い円を表示する
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 4 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // 交差しない
{
circle.draw(Palette::Gray);
}
// triangle と line の交差情報を取得する
if (const auto points = triangle.intersectsAt(line))
{
triangle.draw(Palette::Skyblue);
// 交差する座標に赤い円を表示する
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 4 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // 交差しない
{
triangle.draw(Palette::Gray);
}
line.draw(2, Palette::Seagreen);
}
}
24.8 長方形が重なる領域を取得する¶
2 つの長方形 a と b が重なる領域を a.getOverlap(b) で取得できます。この関数の戻り値は Rect または RectF で、重なる領域がない場合は空の長方形(大きさが 0 の長方形)を返します。
ある長方形 rect が空であるかは if (rect.isEmpty()), if (rect), if (not rect) などで判定できます。
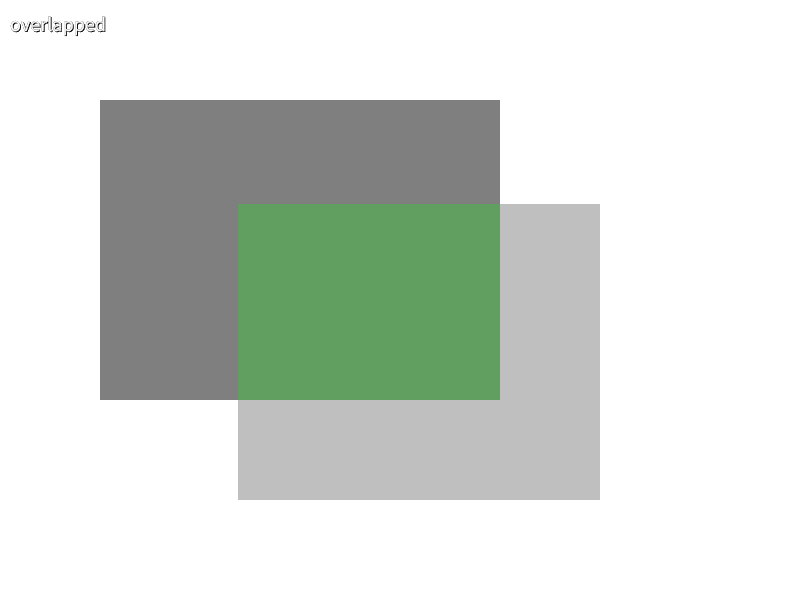
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(Palette::White);
const Rect rect1{ 100, 100, 400, 300 };
while (System::Update())
{
ClearPrint();
const Rect rect2 = Rect::FromPoints(Cursor::Pos(), Point{ 600, 500 });
rect1.draw(ColorF{ 0.5 });
rect2.draw(ColorF{ 0.75 });
// 2 つの長方形が重なる領域を Rect で返す
if (const auto overlap = rect1.getOverlap(rect2))
{
Print << U"overlap";
overlap.draw(ColorF{ 0.0, 0.5, 0.0, 0.5 });
}
}
}