45. 図形の交差判定¶
図形のクリック判定や、交差判定を行う方法を学びます。
45.1 マウスオーバー¶
- 各図形クラスのメンバ関数
.mouseOver()を使うと、その図形の上にマウスカーソルがあるかを調べることができます .mouseOver()はその図形の上にマウスカーソルがある場合に true を返します- 図形が実際に描画されているかは結果に影響しません
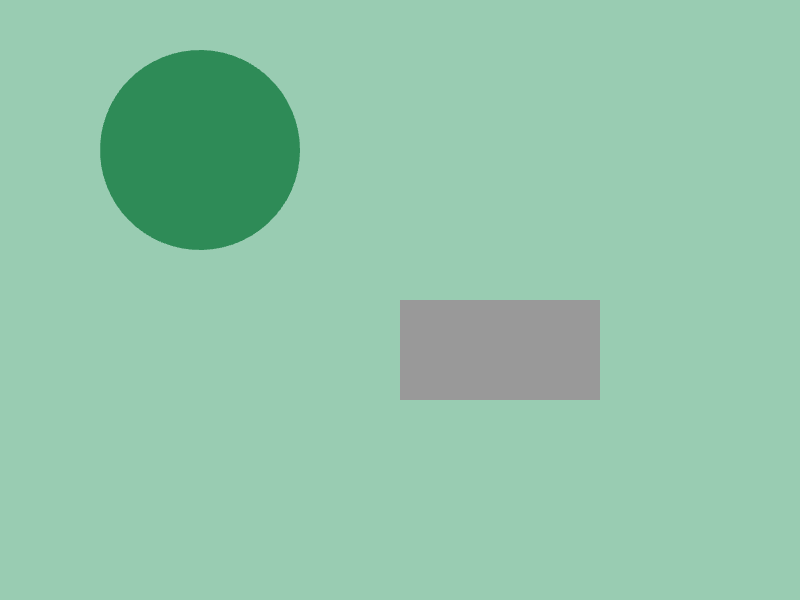
マウスカーソルが図形の上にある場合、図形の色を変える
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Circle circle{ 200, 150, 100 };
const Rect rect{ 400, 300, 200, 100 };
while (System::Update())
{
circle.draw(circle.mouseOver() ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
rect.draw(rect.mouseOver() ? ColorF{ 0.8 } : ColorF{ 0.6 });
}
}
45.2 図形のクリック¶
- 各図形クラスには、クリック判定を行う次のようなメンバ関数が用意されています
| コード | 説明 |
|---|---|
.leftClicked() |
図形上でマウスの左ボタンを押したか |
.leftPressed() |
図形上でマウスの左ボタンを押しているか |
.leftReleased() |
図形上でマウスの左ボタンを離したか |
.rightClicked() |
図形上でマウスの右ボタンを押したか |
.rightPressed() |
図形上でマウスの右ボタンを押しているか |
.rightReleased() |
図形上でマウスの右ボタンを離したか |
- click, pressed, released の関係は、
Inputの.down(),.pressed(),.up()と同じです- 例えば、
.leftClicked()は、クリックしたフレームのみtrueを返します .leftPressed()は、クリックしたフレームだけでなく、それ以降押され続けている場合にもtrueを返します.leftReleased()は、クリックが離されたフレームのみtrueを返します
- 例えば、
- マウスのボタンを押しながら図形の範囲外にカーソルを移動した場合、
.leftPressed()はtrueを返しません - 図形の範囲外でボタンを離した場合、
.leftReleased()はtrueを返しません
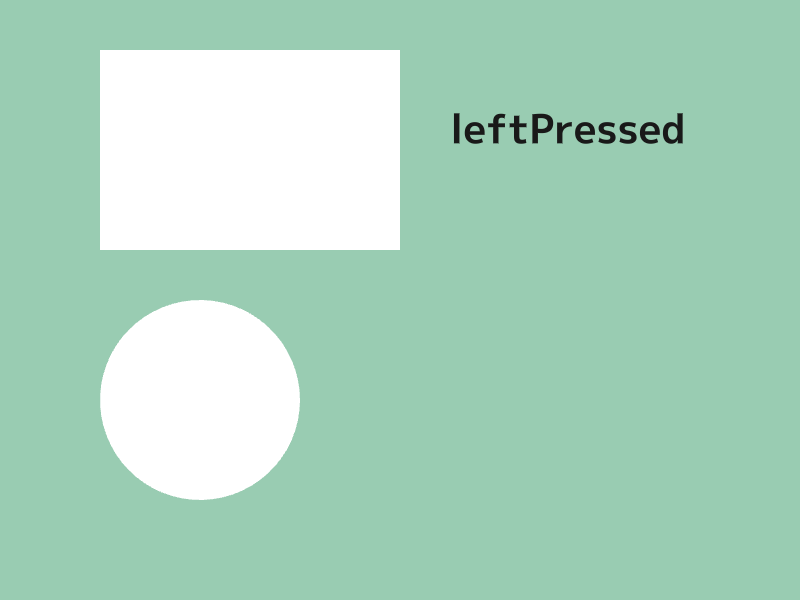
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Font font{ FontMethod::MSDF, 48, Typeface::Bold };
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 300, 200 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
while (System::Update())
{
rect.draw();
circle.draw();
if (rect.leftClicked())
{
font(U"leftClicked").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 50 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (rect.leftPressed())
{
font(U"leftPressed").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 100 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (rect.leftReleased())
{
font(U"leftReleased").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 150 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (circle.leftClicked())
{
font(U"leftClicked").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 350 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (circle.leftPressed())
{
font(U"leftPressed").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 400 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
if (circle.leftReleased())
{
font(U"leftReleased").draw(40, Vec2{ 450, 450 }, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
}
45.3 図形の交差¶
- 2 つの図形
aとbが交差しているかは、a.intersects(b)で調べられます - 異なる図形クラス間で判定可能です
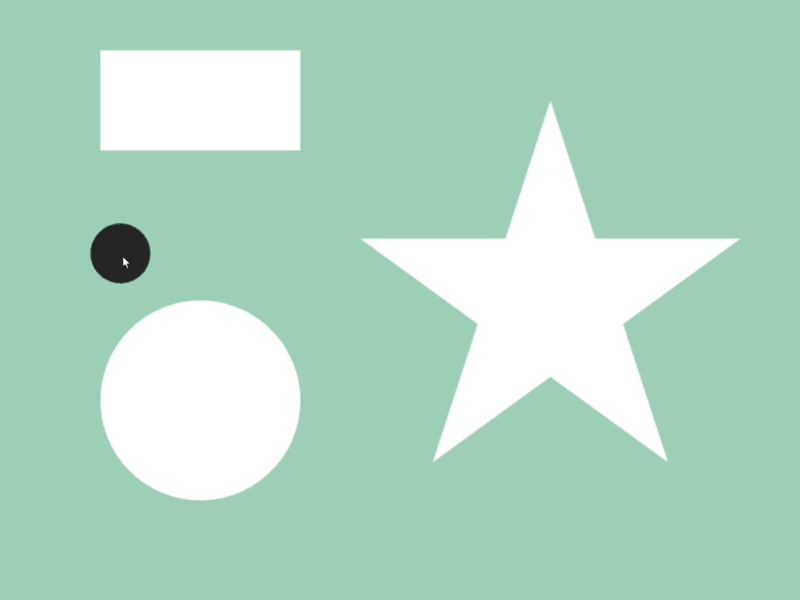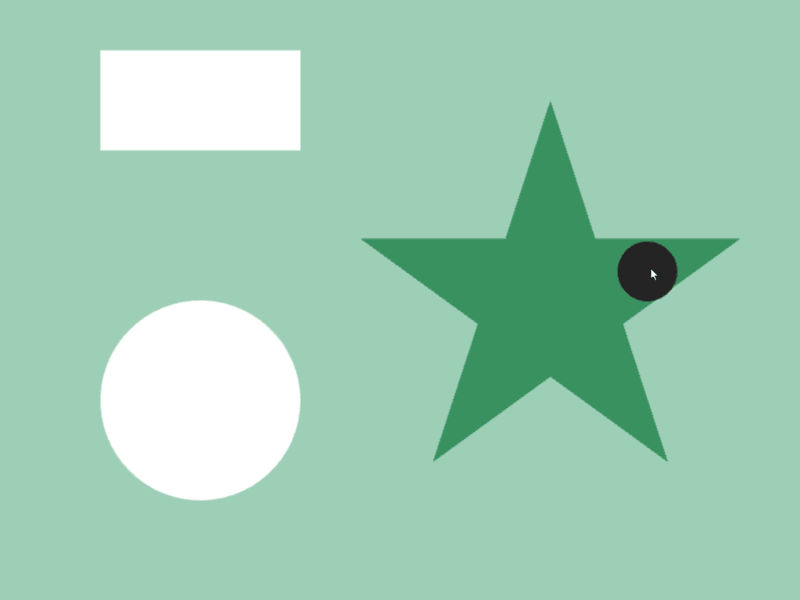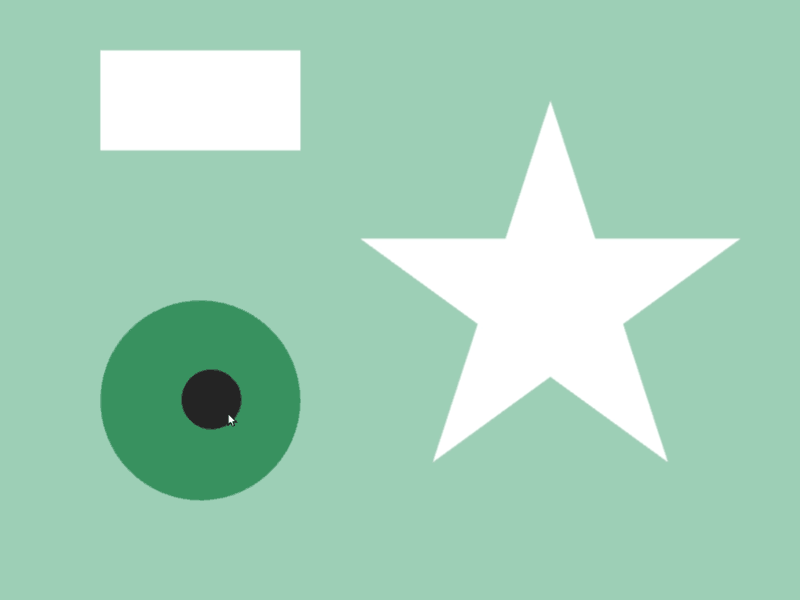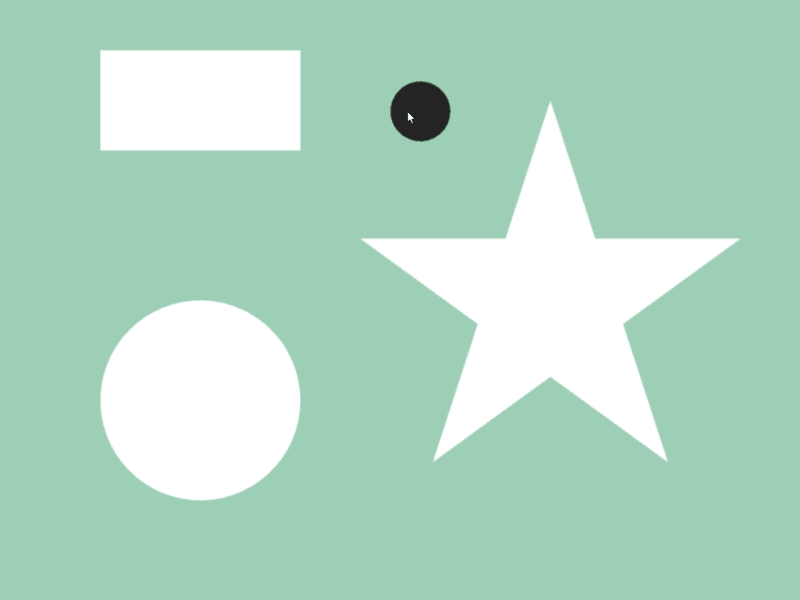
- 次のサンプルでは、マウスカーソルに追従する円が長方形や星などの図形と重なっているときに、その図形の色を変化させます
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 550, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Circle c{ Cursor::Pos(), 30 };
rect.draw(rect.intersects(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
circle.draw(circle.intersects(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
star.draw(star.intersects(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
c.draw(ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.4 図形を内側に含む¶
- ある図形
aが別の図形bを完全に内側に含んでいるかは、a.contains(b)で調べられます - 異なる図形クラス間で判定可能です
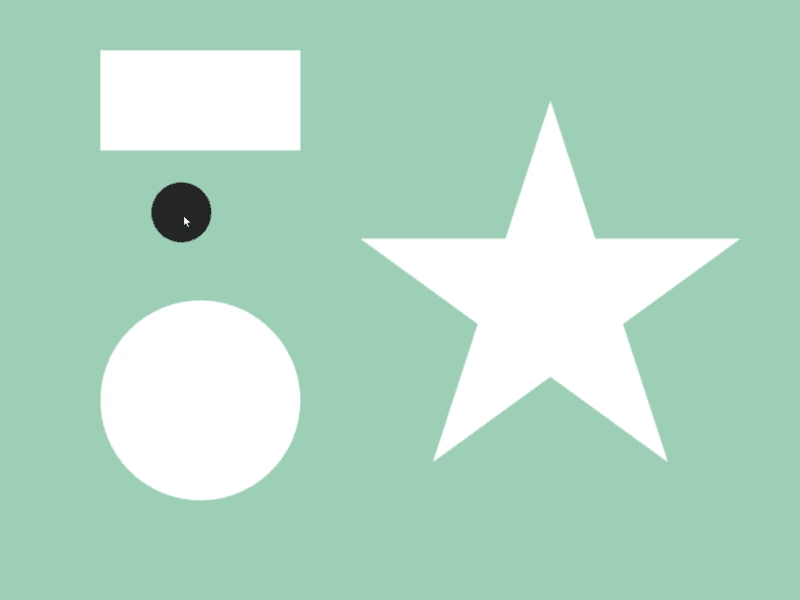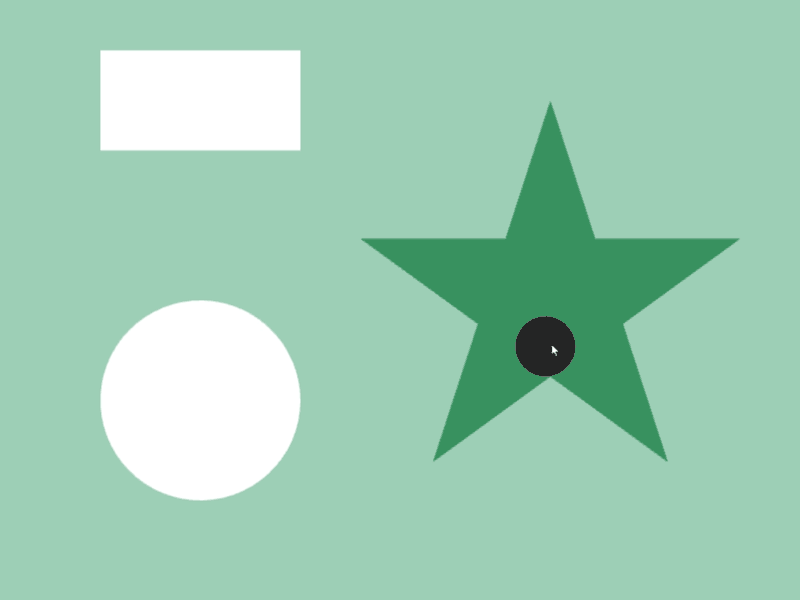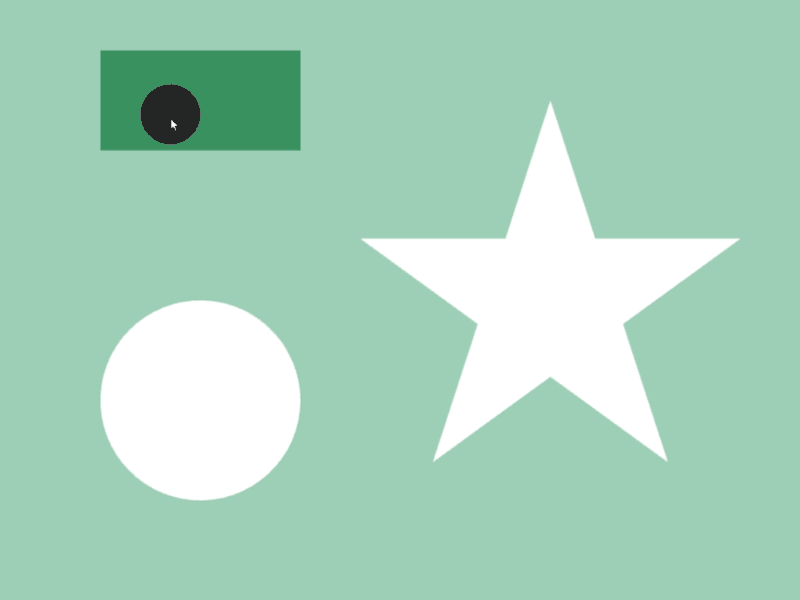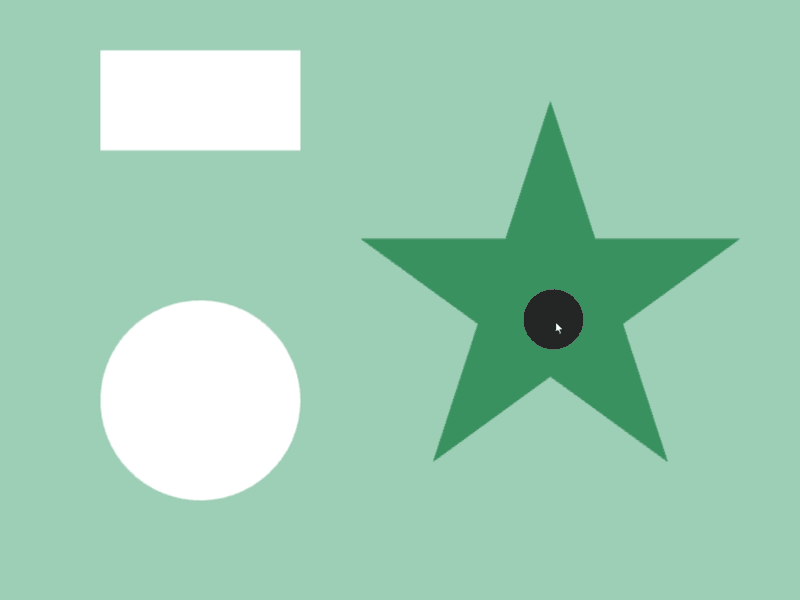
- 次のサンプルでは、マウスカーソルに追従する円が長方形や星などの図形の内部に完全に含まれているときに、その図形の色を変化させます
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 550, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Circle c{ Cursor::Pos(), 30 };
rect.draw(rect.contains(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
circle.draw(circle.contains(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
star.draw(star.contains(c) ? Palette::Seagreen : Palette::White);
c.draw(ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.5 線分どうしの交差位置取得¶
- 2 つの線分
a,bの交差情報をa.intersectsAt(b)で取得できます - この関数の戻り値は
Optional<Vec2>で、交差の状況に応じて次のような値になります
| 交差の状況 | 戻り値 |
|---|---|
| 交差していない | none |
| 交差している | Vec2{ 交点の座標 } |
| 平行に重なっている | Vec2{ QNaN, QNaN } |
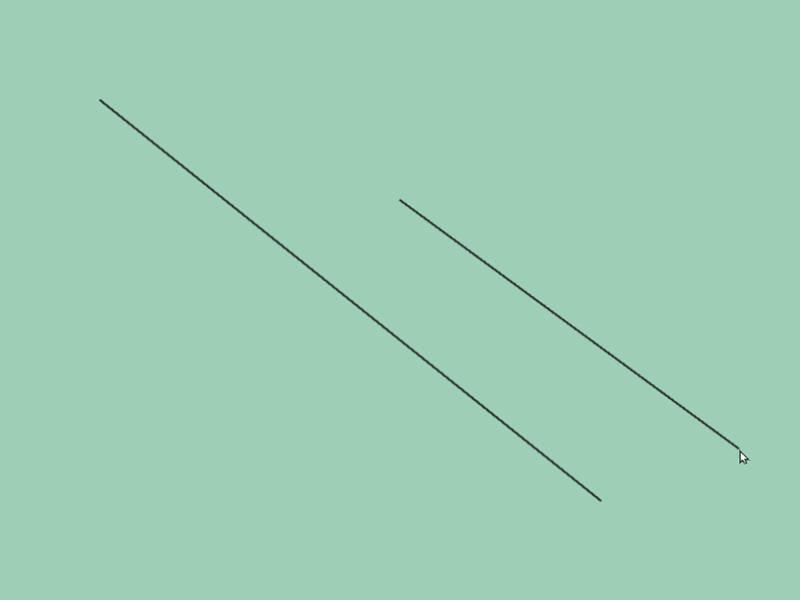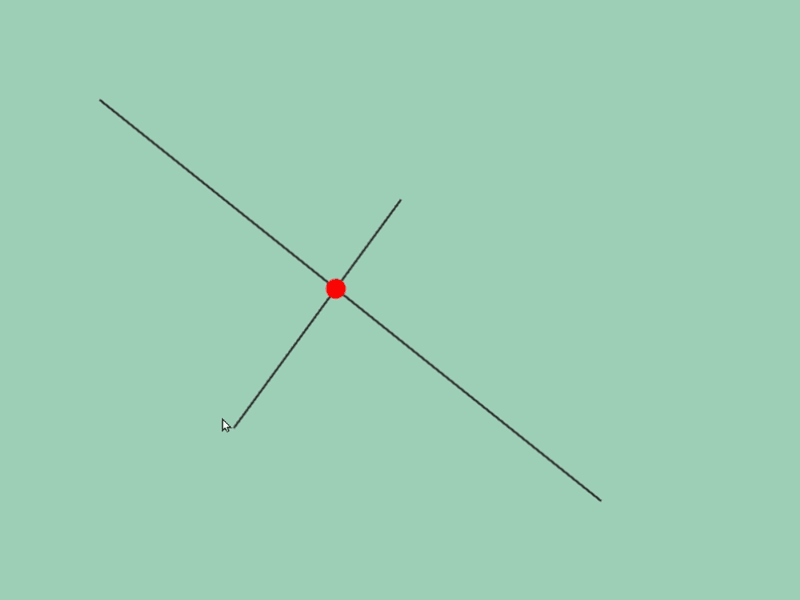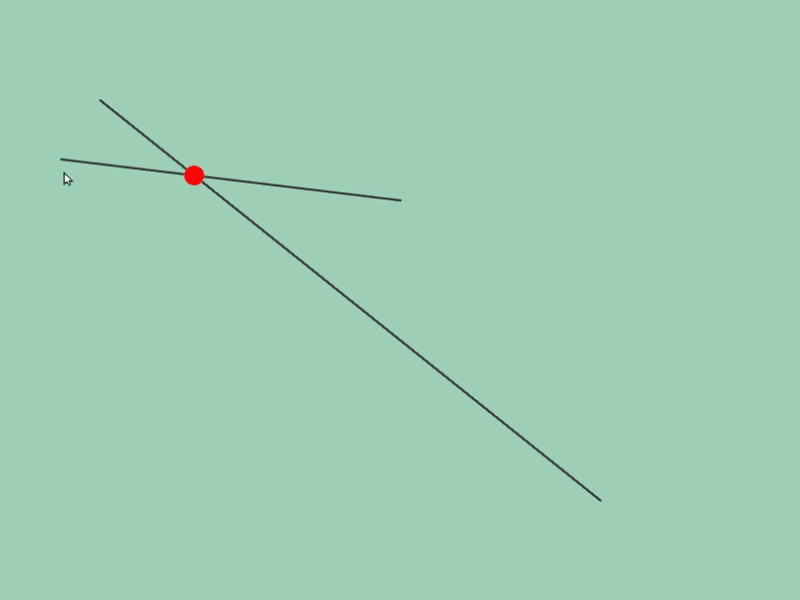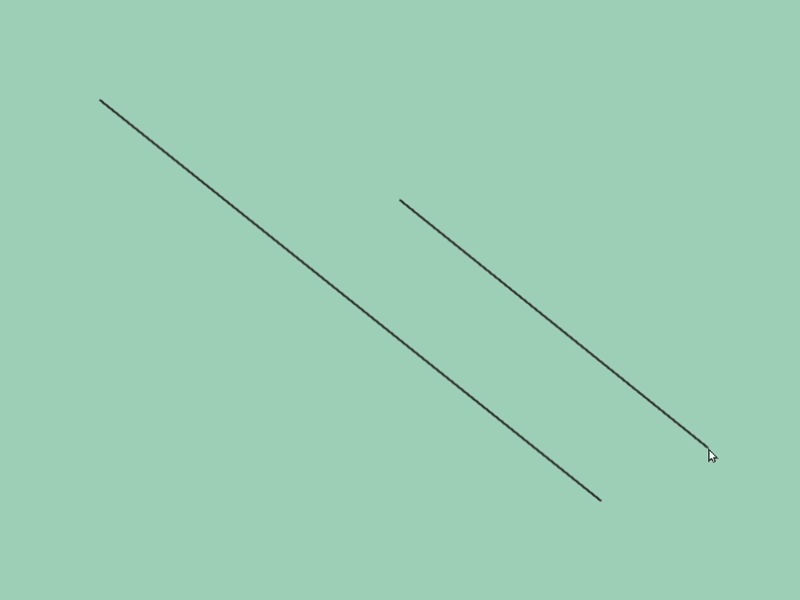
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Line line1{ 100, 100, 600, 500 };
while (System::Update())
{
const Line line2{ 400, 200, Cursor::Pos() };
line1.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
line2.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
if (const auto& intersection = line1.intersectsAt(line2))
{
Circle{ *intersection, 10 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
}
- 2 つの線分が平行に重なっているケースを、次のコードで確認できます
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
const Line line1{ 100, 100, 200, 200 };
const Line line2{ 100, 100, 300, 300 };
if (const auto intersection = line1.intersectsAt(line2))
{
Print << *intersection;
// 交点が NaN なら、2 つの線分は重なっている
if (intersection->hasNaN())
{
Print << U"Two lines are overlapped.";
}
}
while (System::Update())
{
}
}
45.6 図形と図形の交差位置取得¶
- 2 つの図形
a,bの交差情報をa.intersectsAt(b)で取得できます - 異なる図形クラス間で判定可能です
- この関数の戻り値は
Optional<Array<Vec2>>で、交差の状況に応じて次のような値になります
| 交差の状況 | 戻り値 |
|---|---|
| 交差していない | none |
| 交差している | Array<Vec2>{ 交点の座標, ... } |
| 交差しているが交点を求められなかった(内部に含まれるといったケース) | Array<Vec2>{}(空の配列) |
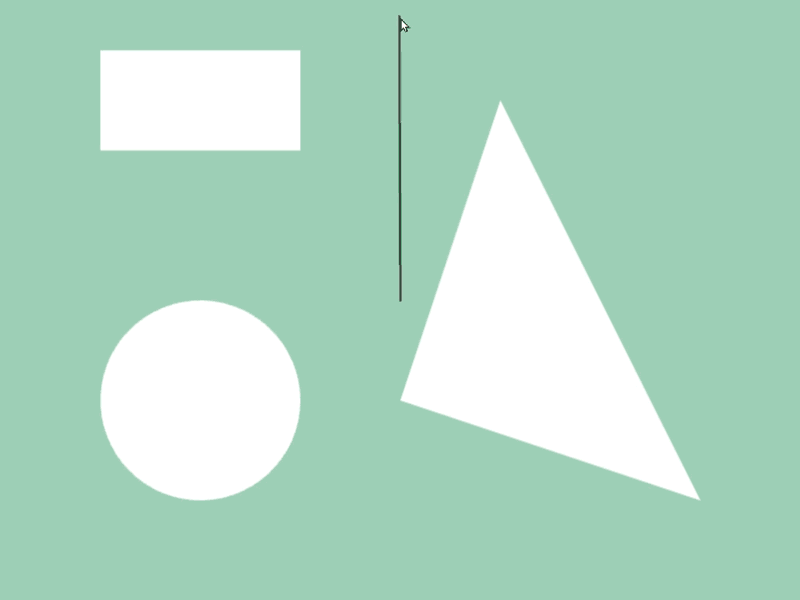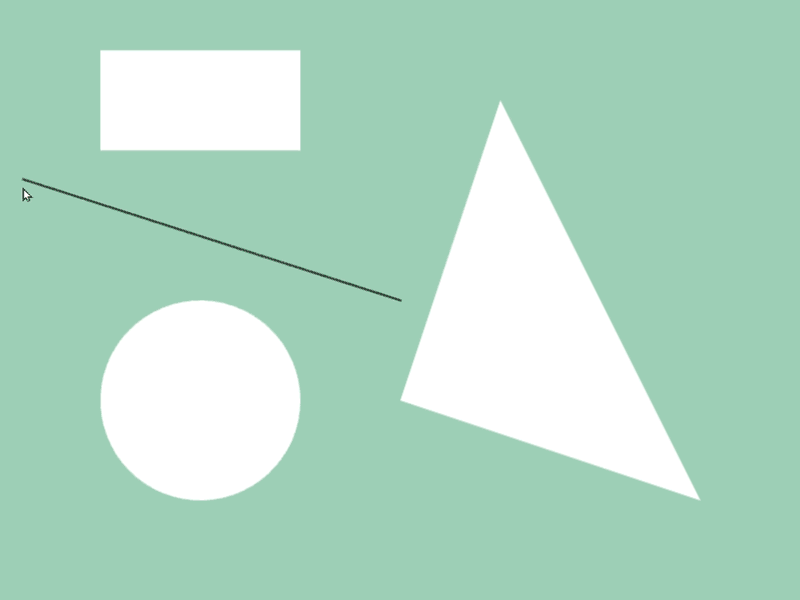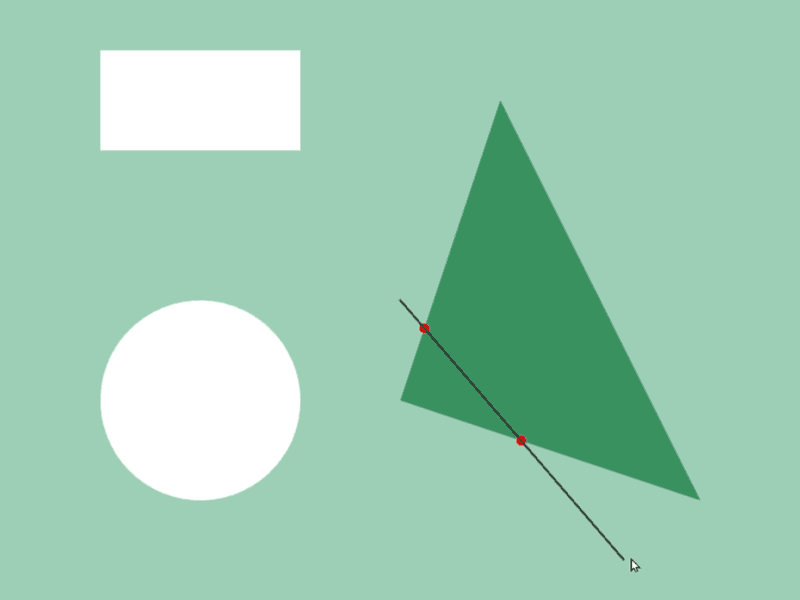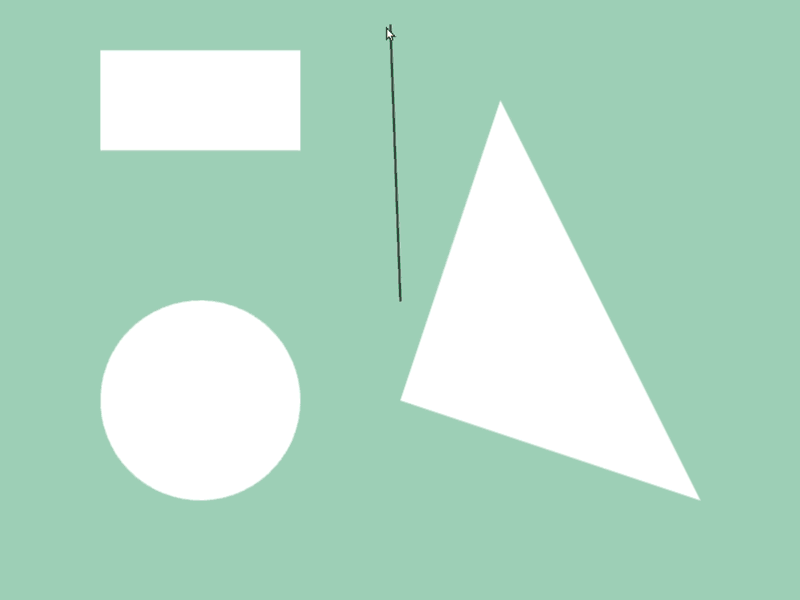
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect{ 100, 50, 200, 100 };
const Circle circle{ 200, 400, 100 };
const Triangle triangle{ Vec2{ 500, 100 }, Vec2{ 700, 500 }, Vec2{ 400, 400 } };
while (System::Update())
{
const Line line{ 400, 300, Cursor::Pos() };
// rect と line の交差情報
if (const auto points = rect.intersectsAt(line))
{
rect.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
// 交差する座標に赤い円を表示する
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 5 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // 交差しない
{
rect.draw();
}
// circle と line の交差情報
if (const auto points = circle.intersectsAt(line))
{
circle.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
// 交差する座標に赤い円を表示する
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 5 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // 交差しない
{
circle.draw();
}
// triangle と line の交差情報
if (const auto points = triangle.intersectsAt(line))
{
triangle.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
// 交差する座標に赤い円を表示する
for (const auto& point : *points)
{
Circle{ point, 5 }.draw(Palette::Red);
}
}
else // 交差しない
{
triangle.draw();
}
line.draw(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.7 長方形が重なる領域の取得¶
- 2 つの長方形
a,bが重なる領域をa.getOverlap(b)で取得できます - この関数の戻り値は
RectまたはRectFで、重なる領域がない場合は空の長方形(大きさが 0 の長方形)を返します - ある長方形
rectが空であるかはif (rect.isEmpty()),if (rect),if (not rect)などで判定できます
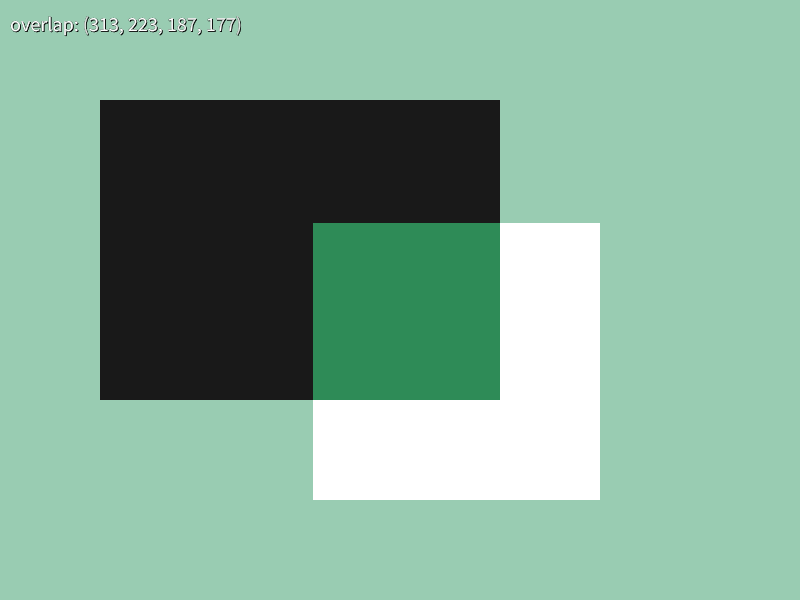
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Rect rect1{ 100, 100, 400, 300 };
while (System::Update())
{
ClearPrint();
const Rect rect2 = Rect::FromPoints(Cursor::Pos(), Point{ 600, 500 });
rect1.draw(ColorF{ 0.1 });
rect2.draw();
// 2 つの長方形が重なる領域を Rect で返す
if (const auto overlap = rect1.getOverlap(rect2))
{
Print << U"overlap: " << overlap;
overlap.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
}
}
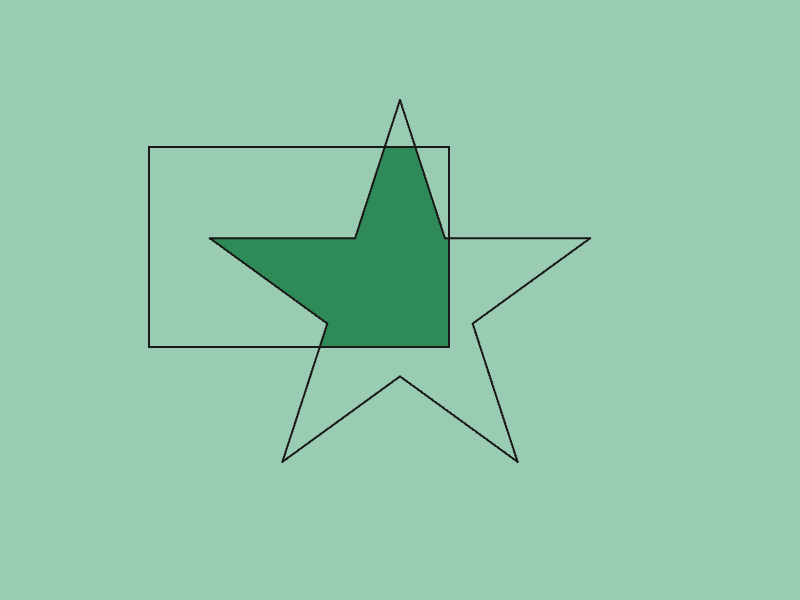
45.8 多角形の AND¶
- 2 つの
Polygona,bの積集合(共通部分)をGeometry2D::And(a, b)で取得できます - 戻り値は
Array<Polygon>で、共通部分がない場合は空の配列を返します
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 400, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Polygon rect = Rect{ Cursor::Pos(), 300, 200 }.asPolygon();
const Array<Polygon> polygons = Geometry2D::And(star, rect);
for (const auto& polygon : polygons)
{
polygon.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
star.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
rect.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
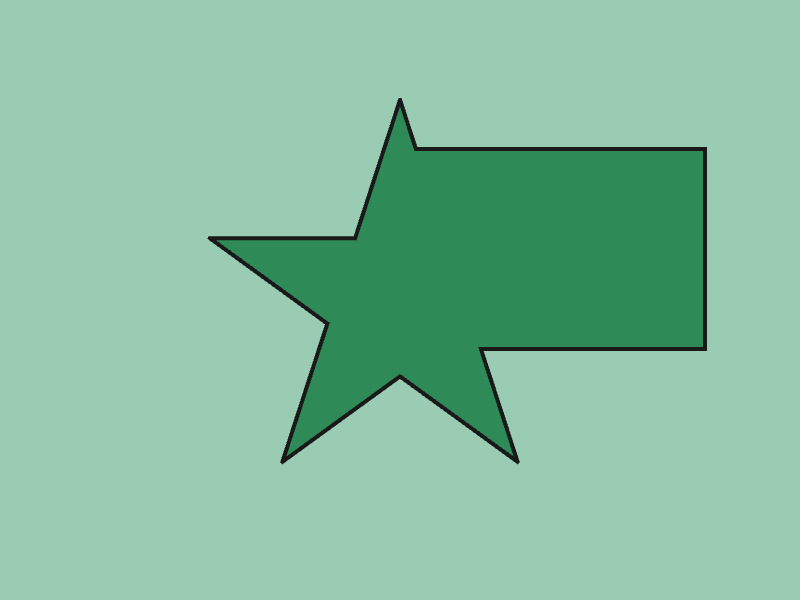
45.9 多角形の OR¶
- 2 つの
Polygona,bの和集合をGeometry2D::Or(a, b)で取得できます - 戻り値は
Array<Polygon>です
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 400, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Polygon rect = Rect{ Cursor::Pos(), 300, 200 }.asPolygon();
const Array<Polygon> polygons = Geometry2D::Or(star, rect);
for (const auto& polygon : polygons)
{
polygon.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
polygon.drawFrame(4, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
}
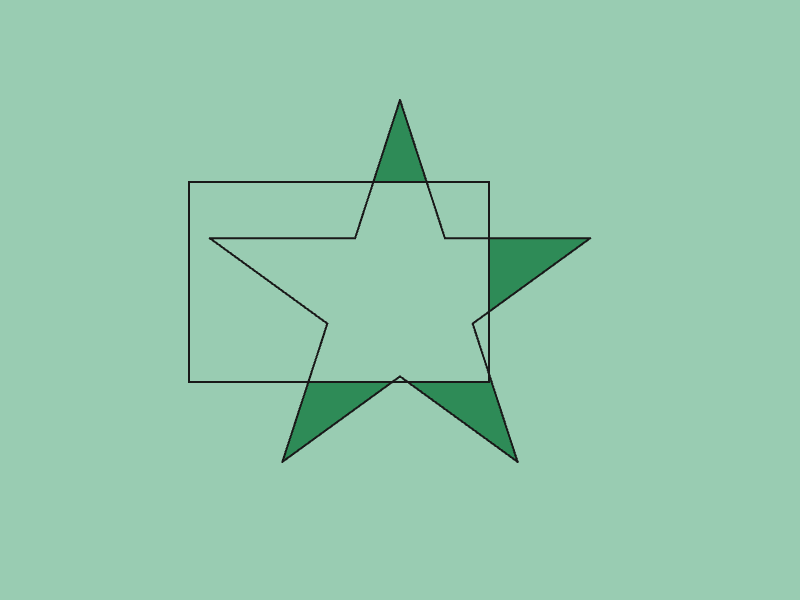
45.10 多角形の差¶
- 2 つの
Polygona,bの差(aからbと重なる部分を取り除いたもの)をGeometry2D::Subtract(a, b)で取得できます - 戻り値は
Array<Polygon>です
# include <Siv3D.hpp>
void Main()
{
Scene::SetBackground(ColorF{ 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 });
const Polygon star = Shape2D::Star(200, Vec2{ 400, 300 });
while (System::Update())
{
const Polygon rect = Rect{ Cursor::Pos(), 300, 200 }.asPolygon();
const Array<Polygon> polygons = Geometry2D::Subtract(star, rect);
for (const auto& polygon : polygons)
{
polygon.draw(Palette::Seagreen);
}
star.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
rect.drawFrame(2, ColorF{ 0.1 });
}
}
45.11 多角形の凸包¶
Polygonクラスには、自身の凸包(すべての頂点を完全に囲む最小の凸多角形)を求めるメンバ関数.computeConvexHull()が用意されています- 戻り値は
Polygonです